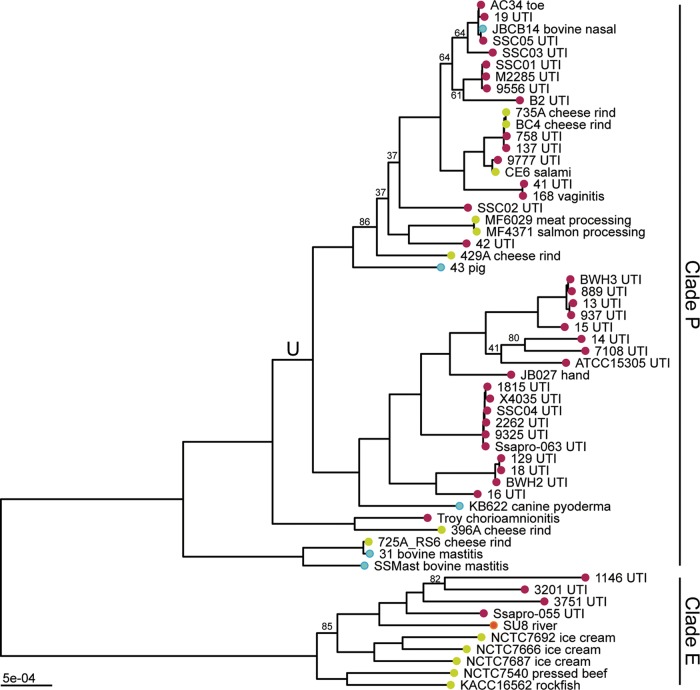
FIG 1 .
Maximum likelihood phylogeny of S. saprophyticus. Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis was performed in RAxML (92) using a whole-genome alignment with repetitive regions masked. The phylogeny is midpoint rooted, and nodes with bootstrap values of less than 90 are labeled. Branch lengths are scaled by the number of substitutions per site. Tips are colored based on the isolation source (pink, human; blue, animal; green, food; orange, environment). Tips are labeled with the isolate name and detailed source information. S. saprophyticus contains two major clades (clade P and clade E). Within clade P, there is a lineage enriched in human-pathogenic isolates (lineage U [branch labeled “U”]).