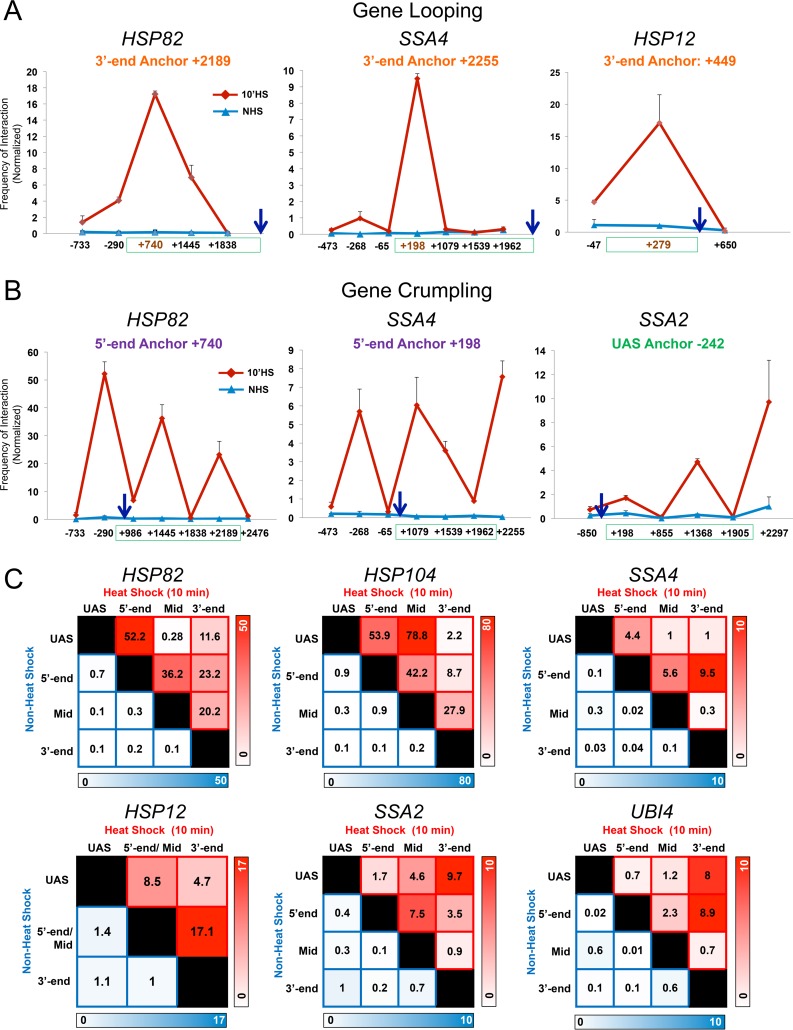
FIG 2.
Heat shock-dependent looping and crumpling is a general feature of HSP genes. (A) HSP genes form prominent 5′-3′ gene loops in response to heat shock. Depicted are normalized 3C interaction frequencies at representative HSP genes under NHS or 10-min HS conditions (strain BY4741). In each case the anchor primer (arrow), corresponding to the gene's 3′ end, was paired with primers abutting TaqI sites located along the coding and upstream regions (red coordinate on x axis corresponds to the TaqI fragment at the gene's 5′ end). In each graph, the green box spans the coding region. Shown are means and SD; n = 2; qPCR = 4. (B) HSP genes crumple in response to heat shock. Intragenic interactions within the indicated genes were detected under NHS and HS states using the indicated anchor primers. Symbols and analysis were the same as those described for panel A. (C) Matrix summaries of intragenic contact frequencies of HSP genes under control and inducing conditions. The upper right triangle corresponds to the frequency of interaction between indicated loci in 10-min heat-shocked cells (red shading); the lower left triangle corresponds to their frequency of interaction in NHS cells (blue shading). The intensity of color is proportional to the frequency of interaction. Regions within each gene are defined in the legend to Fig. 1A. For each pairwise test, n = 2 and qPCR = 4.