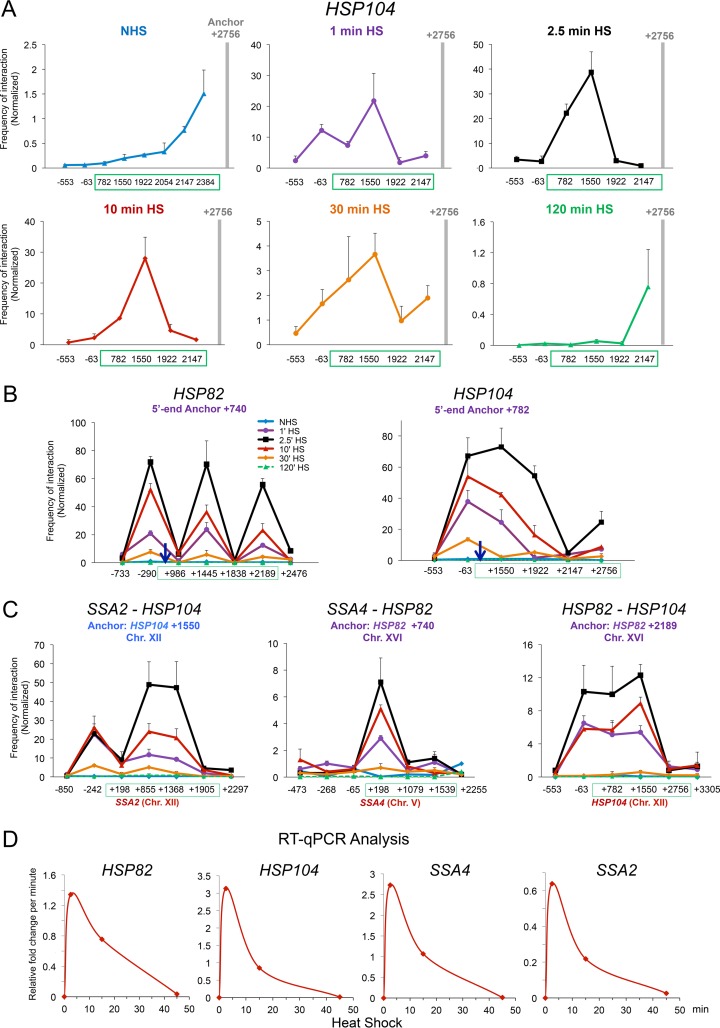
FIG 5.
HSP genes dynamically loop, crumple, and coalesce during heat shock. (A) Heat shock rapidly overrides nonspecific contacts between the anchor and nearby loci, as detected by TaqI-3C. Illustrated is the frequency of intragenic interactions detected within HSP104 over a heat shock time course (note the difference in scale between time points). Analysis and presentation were as described for Fig. 1C. (B) Kinetics of HSP82 and HSP104 looping and crumpling in heat-shocked cells. (Left) 5′-End anchor of HSP82 was paired to the indicated loci upstream, within or downstream of the gene. Normalized 3C interaction frequencies were determined at the times indicated following instantaneous, 30°C to 39°C heat shock. (Right) As above, except the 5′ anchor of HSP104 was paired to the indicated loci. Shown are means and SD; n = 2; qPCR = 4 for each primer combination. (C) Kinetics of intergenic interactions between chromosomally linked and unlinked HSP genes. Analysis and presentation were as described for panel B. (D) Kinetics of HSP gene transcription during heat shock. Depicted is the relative fold change per minute of the indicated mRNAs following a 30°C to 39°C upshift, as deduced from steady-state (RT-qPCR) measurements. Data are consistent with genomic run-on analysis (67).