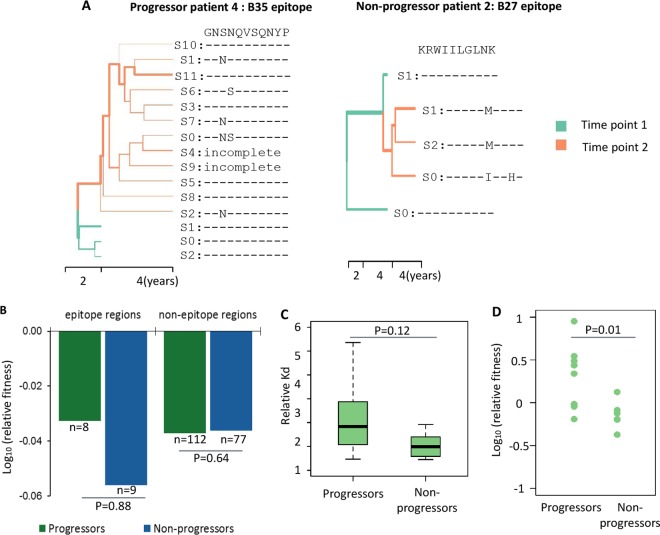
FIG 4 .
HIV intraperson evolution in LTNPs and progressors. (A) Representative phylogenetic trees of virus haplotypes of LTNPs and progressors. Viral haplotypes were assembled by PredictHaplo. Maximum clade credibility (MCC) trees were constructed by BEAST. The mutations in a representative HLA epitope are labeled. The width of branches is proportional to the abundance of the corresponding haplotypes in the population. The colors green and orange represent sampling time point 1 and time point 2. (B) Relative fitness scores of naturally aroused variants in both groups. (C) Predicated effects of epitope mutations in samples on MHC-I binding affinity. For each individual, the epitopes were selected based on the corresponding HLA serotypes. Epitope sequences from all reconstructed viral haplotypes (11 from progressors and 6 from LTNP) were included in the analysis. (D) Relative fitness scores of possible MHC-1 escape mutations in both groups. Possible MHC-I escape mutations from each individual were defined as the ones with levels of binding affinity lower than those seen with the global consensus sequences.