FIG 2 .
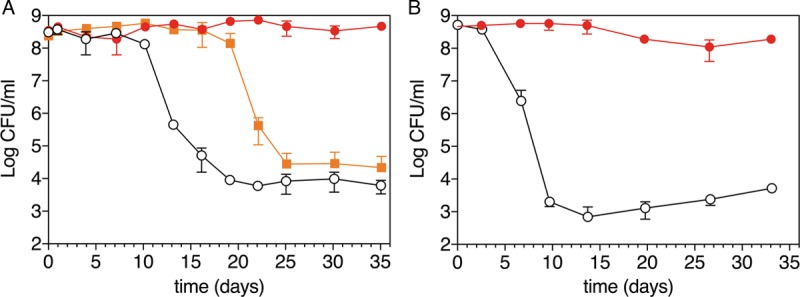
Viability of R. palustris after growth arrest. Growth arrest was initiated by two methods: (A) carbon limitation with N2 gas provided in excess as a nitrogen source or (B) carbon limitation with ammonium provided in excess as the nitrogen source. Growth-arrested cells were incubated anaerobically under constant light (red closed circles) or dark (black open circles) conditions. In panel A, cells were also exposed to 24 h of light following growth arrest and then placed in the dark for the remainder of the experiments (orange closed squares). Viability was measured by plating cells and counting CFU. The averages from two independent experiments are shown for each panel.
