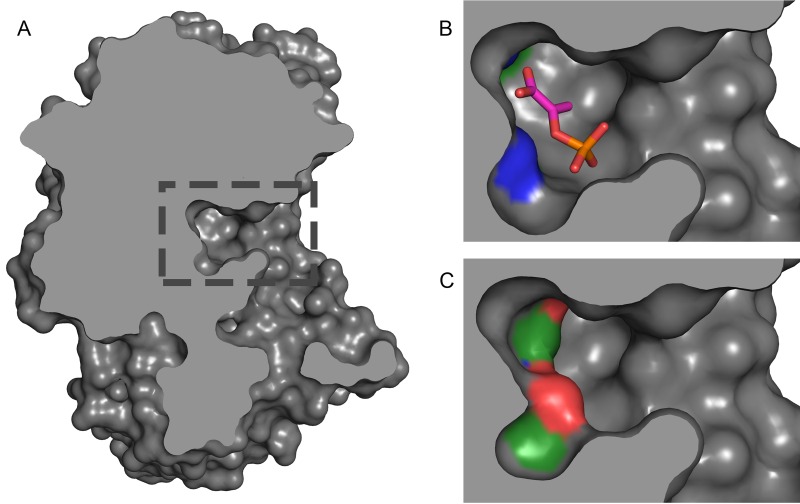
FIG 5 .
Structural change of enolase acetylation. (A) The catalytic binding site of Synechococcus elongatus enolase, PDB 5J04. The boxed region in panel A is enlarged in panels B and C. (B) The binding pocket utilizes two lysine residues (shown in blue at the top and bottom left of the pocket) to bind and stabilize phosphoenolpyruvate (shown as a stick diagram). (C) Acetylating the two active site lysines disrupts both the electrostatic binding potential and the geometry of the binding site, precluding substrate binding.