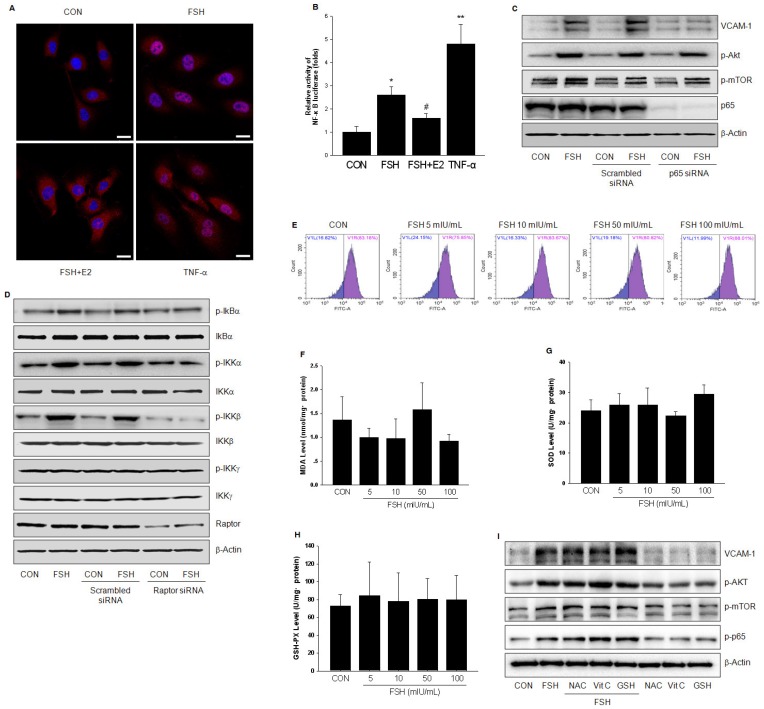
Figure 6.
FSH activated NF-κB signaling through IKK/IkBα pathway. (A). HUVECs were treated with control vehicle (CON), FSH (50 mIU/mL) or TNF-α (0.1 ng/mL) for 24 h in the presence or absence of 17β-estradiol (E2, 10 nM). Subcellular localization of the p65 protein was assayed by immunofluorescence (red staining). Scale bar = 250 μm. (B). HUVECs were transiently transfected with 750 ng of NF-κB-luciferase reporter and 250 ng pRL-TK vector expressing renella luciferase. Subsequently, cells were treated with control vehicle (CON), FSH (50 mIU/mL) or TNF-α (0.1 ng/mL) for 24 h in the presence or absence of 17β-estradiol (E2, 10 nM). Relative luminescent units (RLU) were examined and were normalized to fold change from control. * = P < 0.05, ** = P<0.01 vs. control; # = P<0.05 vs. FSH. (C-D). HUVECs were transfected with scrambled siRNA (100 nM), p65 siRNA (100 nM) (C) or raptor siRNA (100 nM) (D) for 48 h. Cells were then treated with vehicle or FSH (50 mIU/mL) for another 24 h and analyzed by Western blotting. (E). HUVECs were treated with control vehicle (CON) or different concentrations of FSH for 24 h. Then cells were washed and loaded with H2DCFDA and subjected to fluorescence measurement by flow cytometry. V1R gate (right gate) showed the percentage of positive cells loaded with probe. No significance was found between these groups. (F-H). HUVECs were treated as indicated for 24 h and the levels of MDA, SOD, GSH-PX were measured. No significance was found between these groups. (I). HUVECs were treated with control vehicle (CON) or FSH (50 mIU/mL) for 24 h, in the presence or absence of antioxidants (including N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC, 1 mM), Vitamin C (Vit C, 200 μM) and glutathione (GSH, 1 mM)). Proteins were analyzed by Western blotting. All experiments were repeated at least three times with consistent results and the representative images are shown.