Fig. 1.
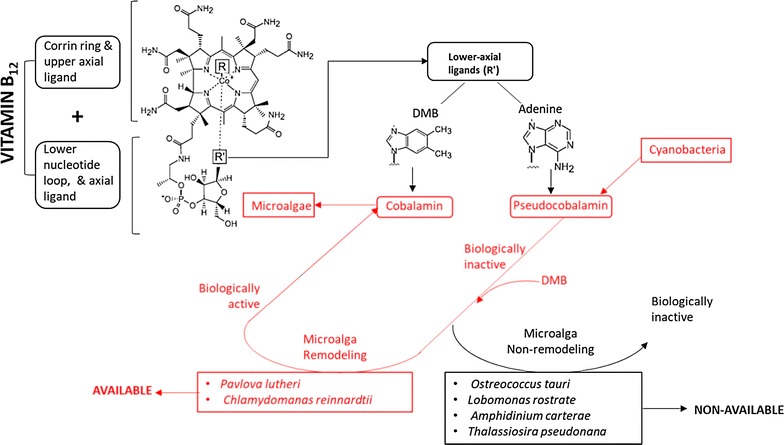
Different components in the chemical structure of vitamin B12 and their modes of transformation from one vitamer (chemical variant), i.e. pseudo cobalamin to another vitamer (chemical variant), i.e. cobalamin. The vitamin B12 consists of corrin ring plus upper ligand and lower nucleotide ring plus axial ligands attached to the cobalt ion. Certain group of microalgae such as Pavlova lutheri and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii could turn the ‘biologically inactive’ pseudocobalamin vitamer into its ‘biologically active’ form, by the term called as “microalgal remodeling”
