Figure 1.
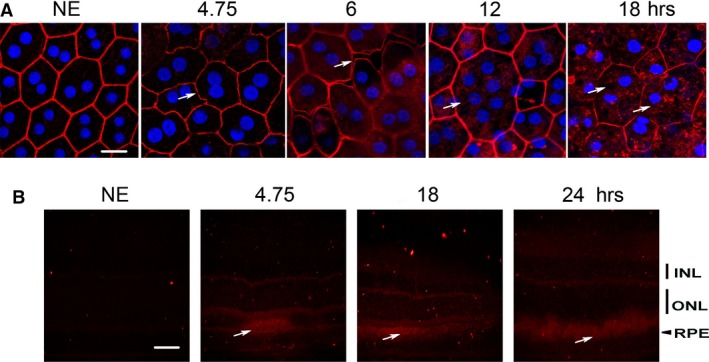
Structural alterations induced by LED exposure. Male Wistar rats aged 7 weeks (n = 4) were exposed to white LED for 4.75, 6, 12, 18, 24 hours receiving the retinal doses of light of 4.14, 5.23, 10.5, 15.7 and 20.9 J/cm2, respectively. NE: Non‐exposed rats. (A) At the end of the exposure period, the RPE was flat‐mounted and stained with phalloidin, which binds to polymerized actin (red) and with DAPI (blue) that labels the nuclei. The white arrows point alterations of the actin cytoskeleton. The RPE was analysed by confocal microscopy. The pictures were taken on the upper retina 100 μm away from the optic nerve. Scale bar represents 10 μm. (B) After LED exposure, the eyes were included in optimal cutting temperature medium (Tissue Tek), cryosectioned and immunostained with anti‐albumin (red). The white arrows point infiltration of albumin in the neuroretina. ONL: outer nuclear layer; INL: inner nuclear layer; RPE: retinal pigment epithelium. Scale bar represents 20 μm.
