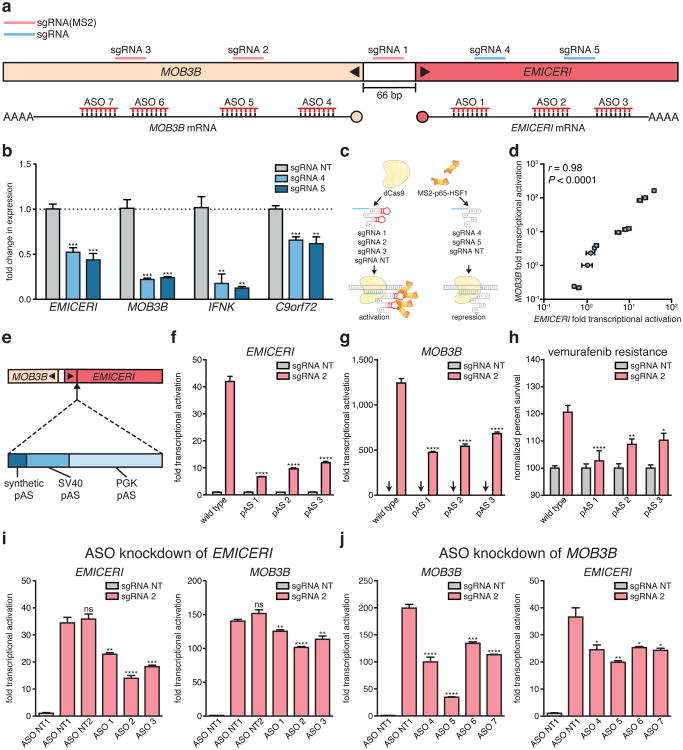
Figure 4. Transcription of EMICERI modulates MOB3B expression.
a, Targeting positions of sgRNAs and antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) in the EMICERI and MOB3B locus. b, Expression of EMICERI and its neighboring genes in A375 cells transduced with non-targeting (NT) or EMICERI-targeting sgRNAs and dCas9. c, Schematic for bimodal perturbation of EMICERI transcription. sgRNAs 1-3 use MS2 loops to recruit MS2-P65-HSF1 to dCas9 to activate EMICERI, whereas sgRNAs 4-5 recruit only dCas9 to repress EMICERI. d, Correlation between MOB3B and EMICERI expression produced by different combinations of sgRNAs with and without MS2 loops. e, Schematic for inserting polyadenylation signals (pAS) downstream of the EMICERI TSS. SV40, Simian virus 40; PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase. f, EMICERI expression after SAM activation of EMICERI for the wild type and pAS clones. g, MOB3B expression after the same perturbations as (f). h, Vemurafenib resistance after SAM activation of EMICERI. i, Expression of EMICERI and MOB3B after ASO knockdown of EMICERI in the context of SAM activation. j, Expression of MOB3B and EMICERI after ASO knockdown of MOB3B in the context of SAM activation. All values are mean ± SEM with n = 4. ****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05. ns = not significant.