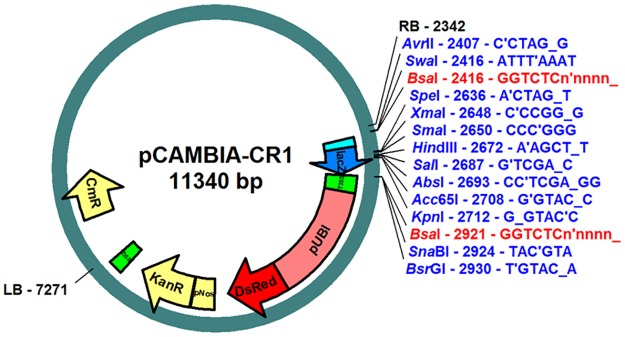
Fig 1. New pCambia Golden Gate vector.
Schematic backbone of the pCAMBIA_CR1 vector showing the BsaI cloning sites (in red) that allow insertion of the oriented blocks using the Golden Gate strategy. Cloning sites (single cutter restriction enzymes or BsaI cloning sites) disrupt the LacZ gene (blue arrow) upon cloning, allowing blue/ white screening with the X-Gal substrate. For E.coli selection, a chloramphenicol (Cm) resistance gene can be used (yellow arrow outside the T-DNA fragment). A kanamycin resistance (kanR) gene, driven by a NOS promoter (yellow box and arrow), enables both selection for the presence of the plasmid in A. rhizogenes and transformed roots on selective medium. The T-DNA contains a pAtUbi:DsRED selection gene (red box and arrow) that allows detection of transformed roots using DsRED fluorescence. RB/LB: T-DNA right border and left border.