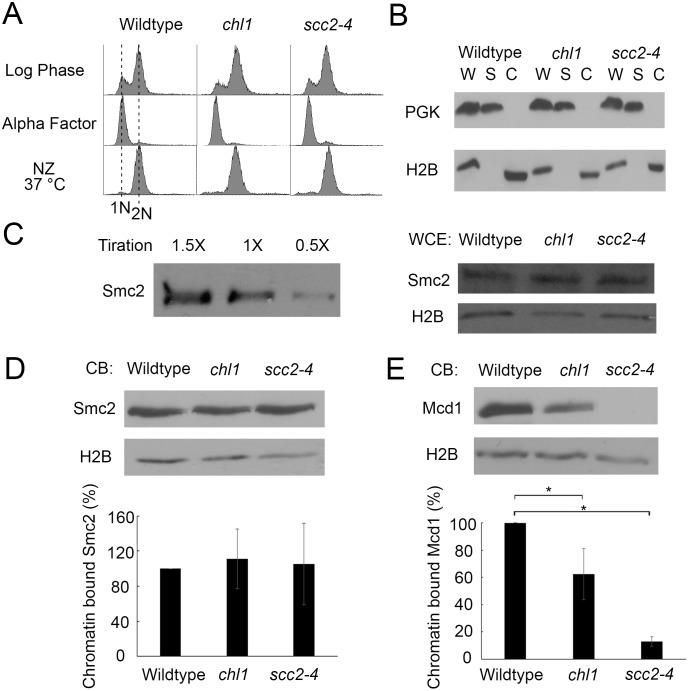
Fig 3. Chl1 helicase promotes chromosome condensation through cohesin, but not condensin, regulation.
A) Flow cytometer data of DNA content throughout the experiment. Cells were maintained in nocodazole for 3 hours at 37°C post-alpha factor arrest. B) Fractionation of preanaphase-arrested wildtype (YDS101), chl1 (YDS104) and scc2-4 (YDS108) cells. Phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) and Histone 2B (H2B) indicate levels of cytoplasmic and chromatin-bound proteins, respectively, in whole cell extracts (W), cytoplasmic soluble fractions (S) and chromatin bound fractions (C). C) Left: Titration of Smc2-HA indicates 1X sample concentration is in the linear range of detection. Right: Whole cell extracts of Smc2-HA in wildtype, chl1 and scc2-4 cells. H2B is shown as internal loading control. All samples reflect 1X concentration levels. D) Top: Chromatin-bound (CB) fraction of Smc2-HA in wildtype, chl1 and scc2-4 cells. Chromatin-bound H2B levels are shown as internal loading control. Bottom: Quantification of Smc2-HA binding to chromatin in chl1 and scc2-4 mutant cells, based on the ratio of Smc2-HA to H2B levels and normalized to wildtype levels of Smc2-HA obtained from 3 biological replicates. E) Top: Chromatin-bound fraction of Mcd1 in wildtype, chl1 and scc2-4 cells. Chromatin-bound H2B levels are shown as loading controls. Bottom: Quantification of Mcd1 binding to chromatin in chl1 and scc2-4 mutant cells, based on the ratio of Mcd1 to H2B levels and normalized to wildtype levels obtained from 3 biological replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey HSD Test. (p = 0.024 for chromatin bound Mcd1 in wildtype versus chl1 mutant cells. p = 0.001 for chromatin bound Mcd1 in wildtype cells versus scc2-4 mutant cells). Statistical significant differences (*) are based on p < 0.05.