Figure 5. Juglanin suppressed lung cancer progression through regulation of NF-κB, PI3K/AKT and MAPKs signaling pathways.
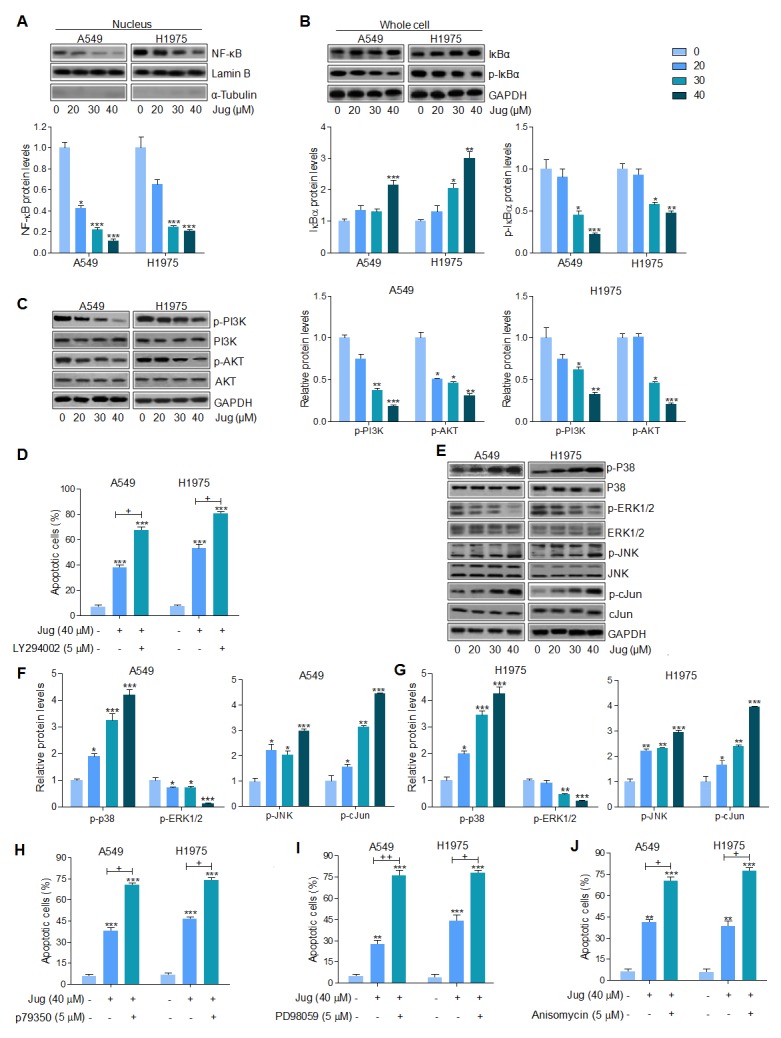
(A) A549 and H1975 cells were treated with different concentrations of juglanin as indicated for 24 h. Then, the nuclues protein was extracted for western blot analysis of NF-κB by the specifc antibody. And Lamin B was applied as the loading control. (B) Total cell extracts were used to detect IκBα and phosphorylated IκBα protein levels. (C) A549 and H1975 cells were administered with different concentrations of juglanin for 24 h, followed by the whole cell protein extracts to calculate p-PI3K and p-AKT levels through western blot assays. (D) The flow cytometry analysis was used to determine apoptotic cells. A549 and HCC 827 cells were treated with 40 μM juglanin with or without PI3K/AKT inhibitor LY294002 (5 μM) for 24 h. (E) A549 and H1975 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of juglanin for 24 h. And western blotting analysis was conducted to determine p-p38, p-ERK1/2 and p-JNK levels. The representative images were shown. The quantification of the immunoblotting results in (F) A549 and (G) H1975 cells. (H) A549 and HCC 827 cells were treated with 40 μM juglanin in the presence or absence of p38 activator p79350 (5 μM) for 24 h. The flow cytometry analysis was performed to detect apoptotic cells. (I) A549 and HCC 827 cells were exposed to 40 μM juglanin with or without ERK1/2 inhibitor 5 μM PD98059 for 24 h. The flow cytometry assay was used to determine apoptotic cells. (J) A549 and HCC 827 cells were treated by the use of 40 μM juglanin with or without JNK activator Anisomycin (5 μM) for 24 h. Apoptotic cells were determined by flow cytometry. The data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. of three separate experiments performed in duplicate. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001 compared to Control group (Con) without any treatment.+ P < 0.05 and ++ P < 0.01 were considered with significant difference.
