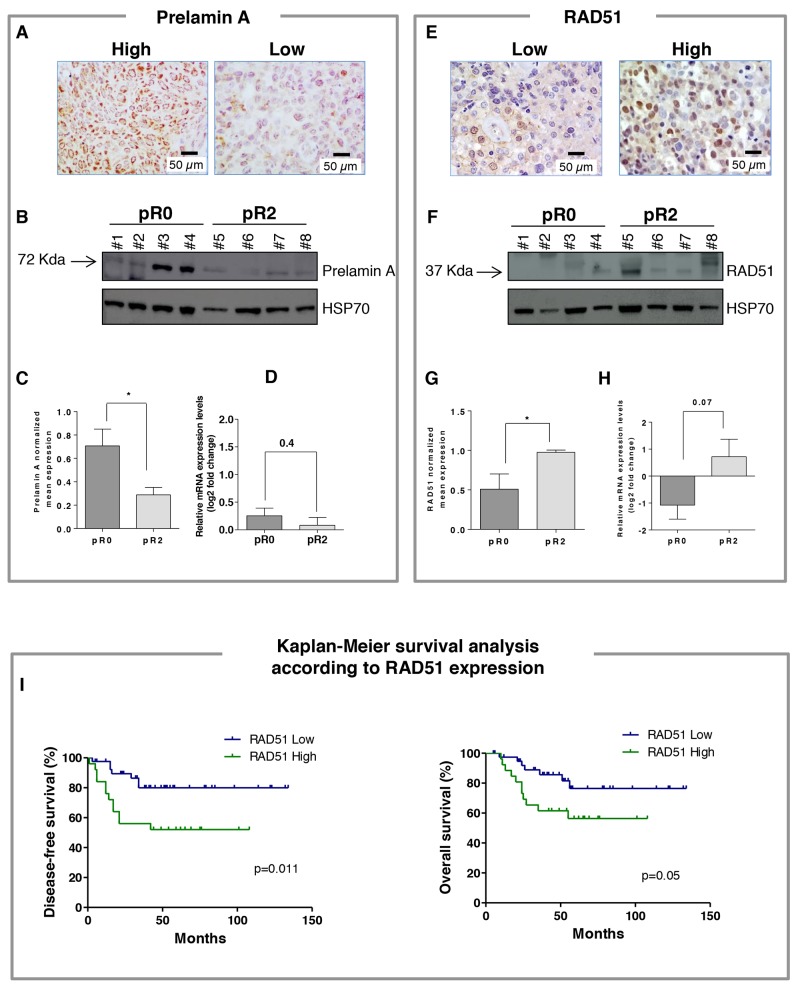
Figure 1.
(A) Representative pictures for high and low prelamin A immunostaining in locally advanced cervical cancer (LACC) patients (magnification 40x). (B) Representative western blot analysis of prelamin A expressions from patients who completely responded to treatment (pR0) and patients with macroscopic residual tumor (pR2) after chemoradiotherapy. #No.= patient code. (C) Densitometric analysis of normalized prelamin A levels respect to HSP70; columns represent the mean ± SEM for each group (n=10 for both groups). Difference was statistically significant between tumors from pR0 and pR2 groups (p < 0.05). (D) The relative mRNA expression of LMNA was evaluated by RT-PCR, utilizing specific set of primers. All samples were normalized to the housekeeping gene, B2M. Results are presented as the mean ± SEM of log2 fold change representative of mRNA expression levels relative to the whole population of samples (n=10 for both groups). (E) Representative pictures for low and high RAD51 immunostaining in LACC patients (magnification 40x). (F) Representative western blot analysis of RAD51 expressions from patients who completely responded to treatment (pR0) and patients with macroscopic residual tumor (pR2) after chemoradiotherapy. #No.= patient code. (G) Densitometric analysis of normalized RAD51 levels respect to HSP70; columns represent the mean ± SEM for each group (n=10 for both groups). Difference was statistically significant between tumors from pR0 and pR2 groups (p < 0.05). (H) The relative mRNA expression of RAD51 was evaluated by RT-PCR, utilizing specific set of primers. All samples were normalized to the housekeeping gene, B2M. Results are presented as the mean ± SEM of log2 fold change representative of mRNA expression levels relative to the whole population of samples (n=10 for both groups). (I) Kaplan–Meier survival curve for the probability of disease-free survival (left) and overall survival (right) according to expression of RAD51 in LACC patients. High expression of RAD51 was significantly associated with disease-free survival and overall survival disadvantage (p = 0.011 and p = 0.05, respectively).