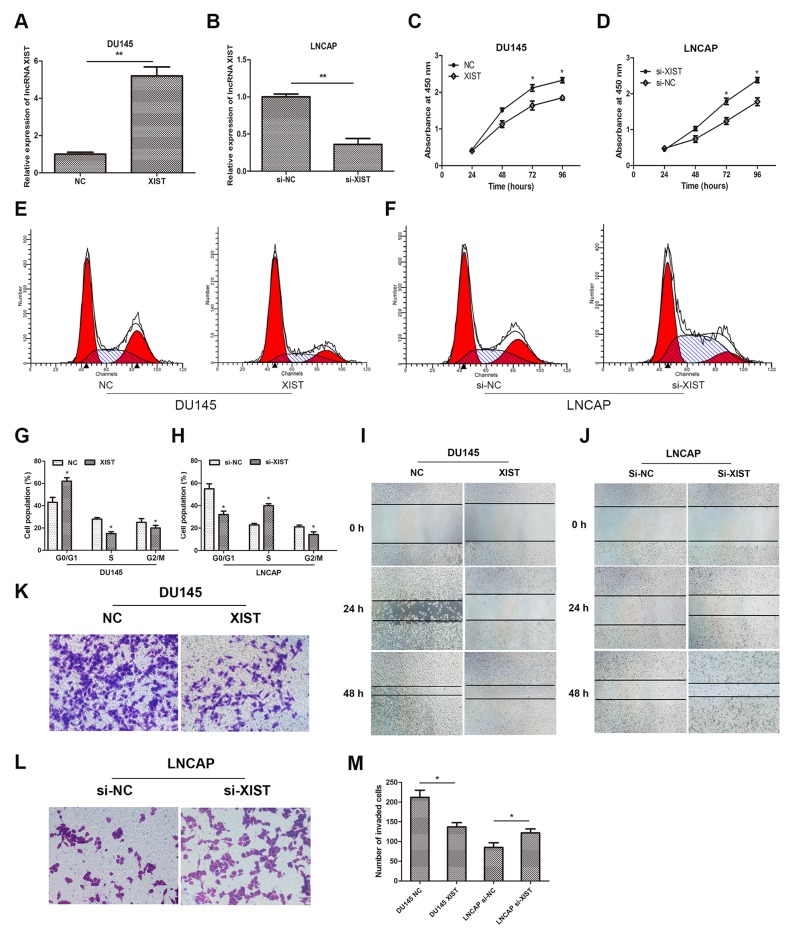
Figure 2. Influence of lncRNA XIST on the malignant phenotypes of prostate cancer in vitro.
(A, B) Relative expression of XIST in DU145 or LNCAP cells after transfection with XIST or si-XIST. **P<0.01 vs. NC group or si-NC group. (C, D) CCK-8 assays were performed to determine cellular proliferation in DU145 cells transfected with XIST and LNCAP cells transfected with si-XIST. *P<0.05 vs. NC group or si-NC group. (E, G) Cell cycle of DU145 cells transfected with XIST or NC was detected by flow cytometry. *P<0.05 vs. NC group. (F, H) Cell cycle of LNCAP cells transfected with si-XIST or si-NC was examined by flow cytometry. *P<0.05 vs. si-NC group. (I, J) Wound healing assays were performed to evaluate cell migratory ability in DU145 cells transfected with XIST or NC and LNCAP cells transfected with si-XIST or si-NC. (K-M) Transwell invasion assays were performed to examine invasive ability in cells. Cell number was counted in five random fields at 200 × magnification. *P<0.05 vs. NC group or si-NC group. Data are presented as mean ± SD from three separated experiments.