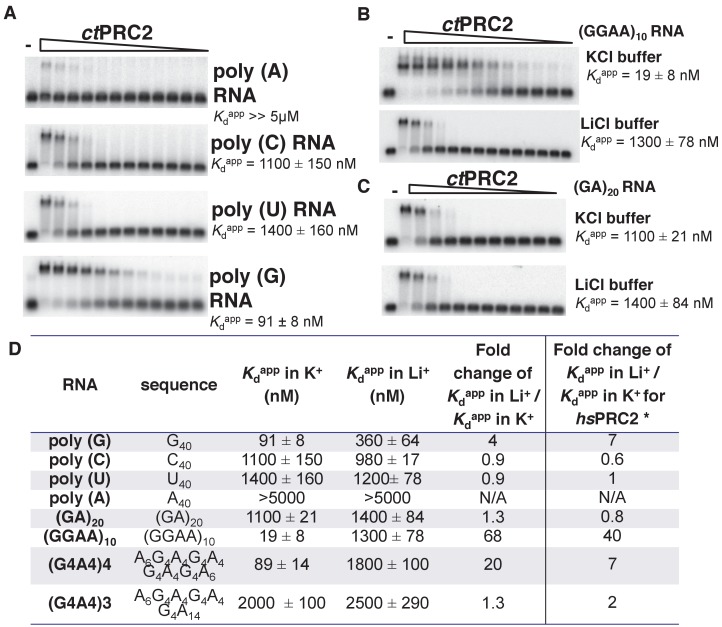
Figure 1. ctPRC2 prefers binding to G-rich RNAs and G-quadruplexes, and shares RNA-binding specificity with hsPRC2.
(A) Binding of ctPRC2 to four 40-mer homopolymeric RNAs was tested using EMSA with standard 100 mM KCl-binding buffer. (B) Binding of ctPRC2 to a G-quadruplex-forming (GGAA)10 RNA was tested in 100 mM KCl and 100 mM LiCl-binding buffers. (C) Binding of ctPRC2 to a control RNA (GA)20 was tested in 100 mM KCl and 100 mM LiCl-binding buffers. (D) Comprehensive analysis of binding affinities of ctPRC2 to a variety of 40-nt RNAs. * Results of this column were from Wang et al. (2017a). For (A), (B) and (C), ctPRC2 was used at successive threefold dilutions starting at 5 µM concentration or 4 µM for (GGAA)10 RNA in KCl buffer. Kdapp values and errors are mean and standard derivation of at least three binding experiments performed on different days and often by a different person.