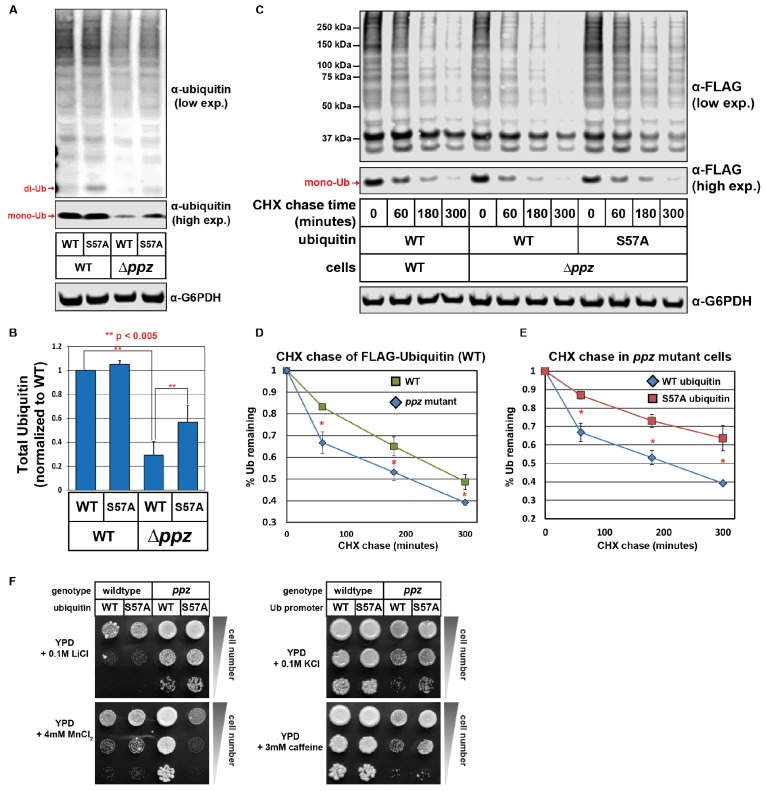
Figure 2. Ser57 phosphorylation of ubiquitin contributes to ppz mutant phenotypes.
(A) Quantitative immunoblot analysis was performed on lysates from wild-type or ppz mutant yeast cells (SUB280 background) expressing either wild-type ubiquitin or Ser57Ala ubiquitin. (B) The results for (A) were quantified over multiple experiments (n = 3). (C) Quantitative immunoblot analysis was performed on lysates from wild-type or ppz mutant yeast cells (SUB280 background) expressing either wild-type ubiquitin or Ser57Ala FLAG-ubiquitin (driven by the TEF1 promoter) following addition of cycloheximide (CHX). (D and E) The results for (C) were quantified over multiple experiments (n = 3). (F) Wild-type and ppz mutant yeast strains (SUB280 background) expressing only wild-type or Ser57Ala ubiquitin were plated in 10-fold serial dilution on the indicated media. Plates were imaged after three days of growth at 26°C. In all panels, double asterisk (**) indicates p<0.005 and single asterisk (*) indicates p<0.05.