Figure 5. Ser57Asp phosphomimetic ubiquitin bypasses an artificial DUB checkpoint.
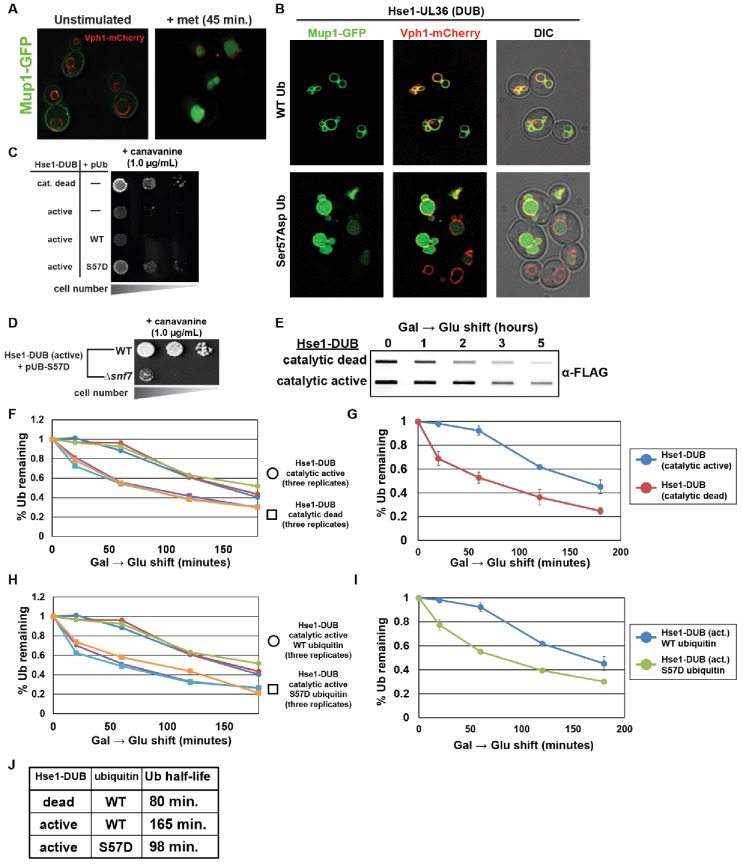
(A) Analysis of Mup1-GFP (green) localization in wildtype yeast cells (strain SEY6210) grown in minimal media lacking methionine (left) or stimulated with methionine for 45 min (right). Cells are stably expressing Vph1-mCherry (red), a marker of the vacuolar membrane. (B) Mup1-GFP localization in yeast cells (strain SEY6210) where the endogenous Hse1 locus has been fused to the UL36 deubiquitylating enzyme, encoding an Hse1-UL36 fusion protein. This creates an artificial DUB checkpoint at ESCRT-0. The top panel of cells are expressing wildtype ubiquitin, whereas the bottom panel of cells are expressing Ser57Asp phosphomimetic ubiquitin. As in (A), cells are stably expressing Vph1-mCherry (red), a marker of the vacuolar membrane. (C and D) Analysis of yeast growth in the presence of canavanine. (E) Slot blot analysis of FLAG-ubiquitin levels following a galactose induction/glucose repression. (F–J) Quantitation of slot blot experiments (as shown in E, n = 3) from yeast cells expressing catalytic active or catalytic dead Hse1-UL36 fusion (F and G) or catalytic active Hse1-UL36 in the presence of wildtype or Ser57Asp phosphomimetic ubiquitin (H and I). Data were averaged over multiple experiments (G and I) (n = 3, error bars indicate standard deviation) and trend line regression was used to calculate ubiquitin half life (J).
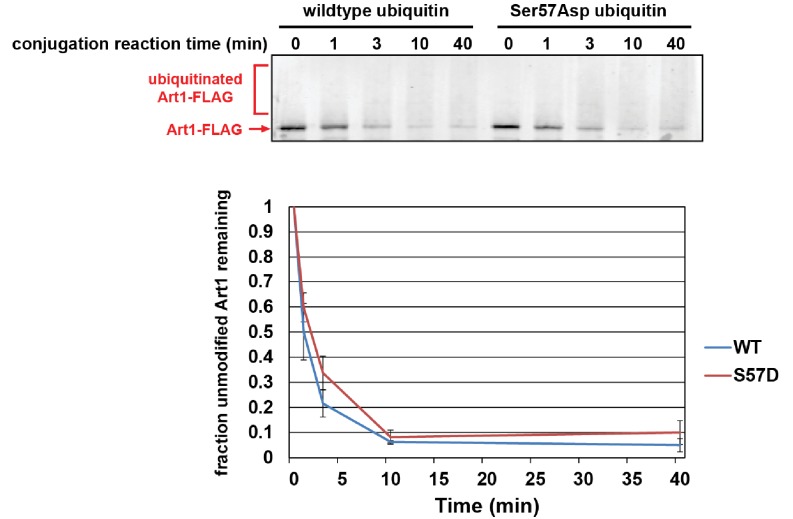
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Ser57Asp phosphomimetic ubiquitin does not alter the rate of Rsp5-mediated conjugation in vitro.
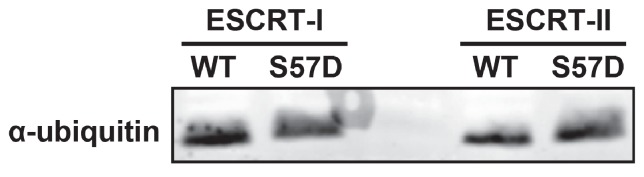
Figure 5—figure supplement 2. Ser57Asp phosphomimetic mutation does not alter binding of ubiquitin to ESCRT-I or ESCRT-II in vitro.
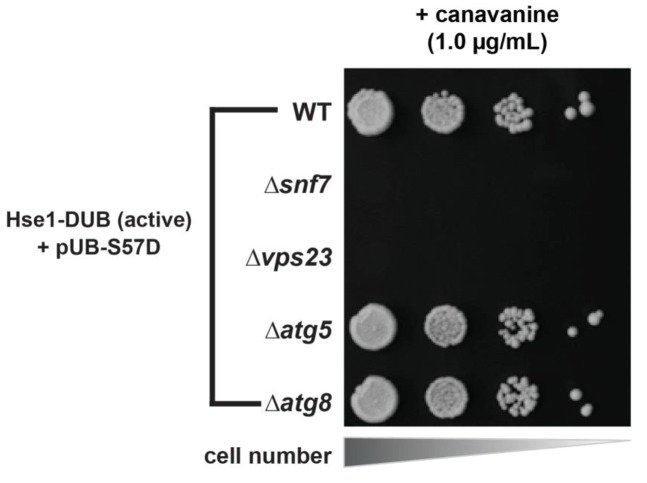
Figure 5—figure supplement 3. DUB bypass by Ser57Asp phosphomimetic ubiquitin requires an in-tact ESCRT pathway while the autophagy pathway is dispensible.
Figure 5—figure supplement 4. Bypass of a Can1-DUB fusion by Ser57Asp phosphomimetic ubiquitin.
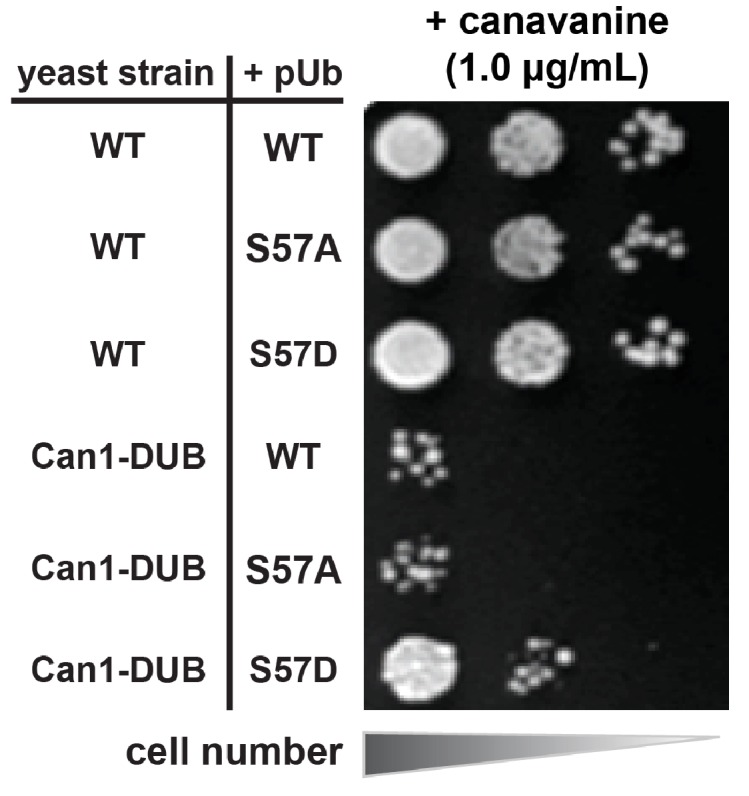
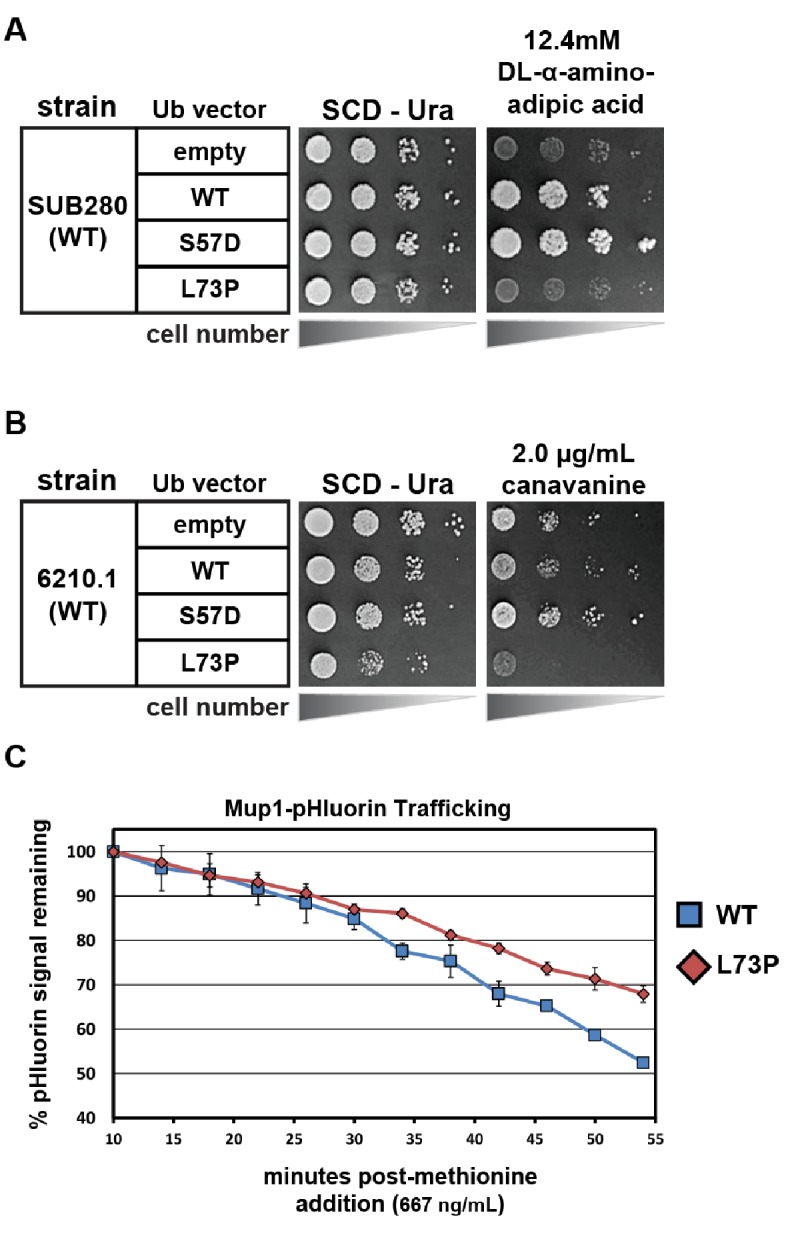
Figure 5—figure supplement 5. Phenotypic analysis of yeast cells expressing Leu73Pro ubiquitin.