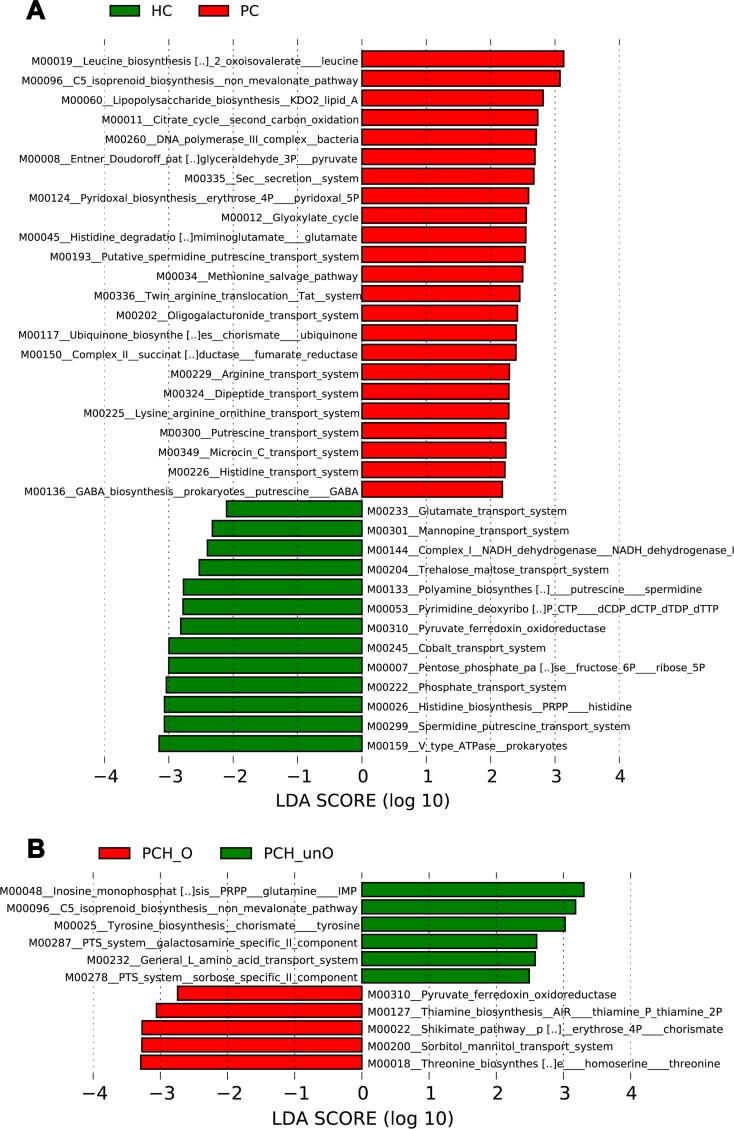
Figure 6. Functional prediction of microbial genes associated with PC using PICRUSt.
(A) The 23 predicted microbial functions including Leucine biosynthesis, Isoprenoid biosynthesis non mevalonate pathway and LPS biosynthesis were significantly enriched, while 13 functions including Type V ATPase in prokaryotes, Spermidine putrescine transport system and Histidine biosynthesis were remarkably reduced in PC patients versus HC, shown by LDA score (log 10). (B) The 6 predicted microbial functions including Inosine monophosphate biosynthesis, C5 isoprenoid biosynthesis non mevalonate pathway and Tyrosine biosynthesis were significantly increased, whereas 5 functions including Threonine biosynthesis, Sorbitol mannitol transport system and Shikimate pathway of phosphoenolpyruvate were decreased in PCH-unO versus PCH-O patients, shown by LDA score (log 10). PICRUSt: Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States; LDA, linear discriminant analysis; HC, healthy controls; PC, pancreatic carcinoma; PCH, PC (head); PCH-O, PCH with obstruction of common bile duct; PCH-unO, PCH with unobstruction of common bile duct.