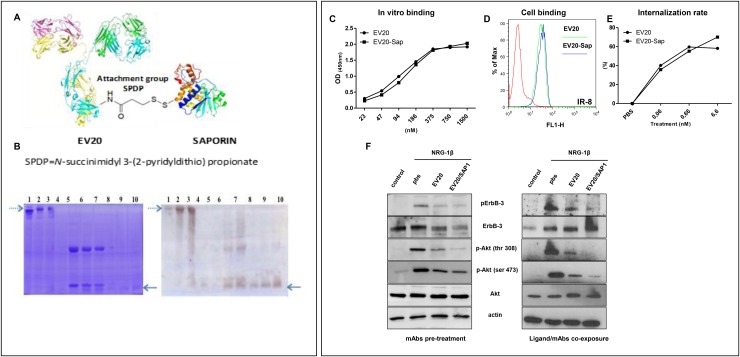
Figure 2. EV20-Sap generation and characterization.
(A) Schematic representation of EV20-Sap. (B) Gel electrophoretic analysis of the EV20-Sap product. EV20-Sap (left panel, lanes 2 and 3, dotted arrow) is to be compared with the free antibody (left panel, lane 1). Under reducing conditions (left panel, lanes 6-7), it is possible to observe the release of the toxin moiety that is absent in the free antibody (left panel, lane 5). Saporin position in gel can be seen in the standards of the toxin present on lanes 8-10 (see full arrow). Western blotting using anti-Saporin antibody reveals the toxin in unreduced EV20-Sap (right panel, lanes 2,3 dotted arrow) and the band corresponding to free Saporin in reduced samples (right panel, lanes 6,7, full arrow). Lanes 4, 8-10: free saporin purified from seeds [250 ng, 500 ng, 1000 ng and 1500 ng]. (C) ELISA showing in vitro binding affinity of naked and Saporin-conjugated EV20 antibody (D) FACS analysis showing cell binding of EV20 and EV20-Sap. (E) Internalization assay. Surface HER-3 receptor analysis measured by FACS. Human melanoma cells were exposed to increasing concentrations of EV20 and EV20-Sap (0.001-0.01-0.1-1-10 μg/ml) for 6 hrs to 37°C, harvested and stained with 1 μg/million of cells of EV20 for 30 min on ice, followed by Alexa Fluor 488 Goat Anti-Human secondary antibody for 30 min on ice, (F) SK-MEL 24 human melanoma cells were starved for 24 hrs and incubated for 2 hrs in presence or absence of 10 μg/ml of EV20 and EV20-Sap, this step was followed by the stimulation with 10 ng/ml of NRG-1β for 5 min (left panel). A375m cells were starved for 24 hrs and incubated simultaneously (15 minutes) with 1 ng/ml of NRG-1β and 10 μg/ml of indicated mAbs (right panel). At the end of the incubation periods, cells were lysed and analysed for pHER-3/HER-3 and pAKT/AKT protein levels by Western blotting. The same filter was reprobed with anti-actin for a loading control.