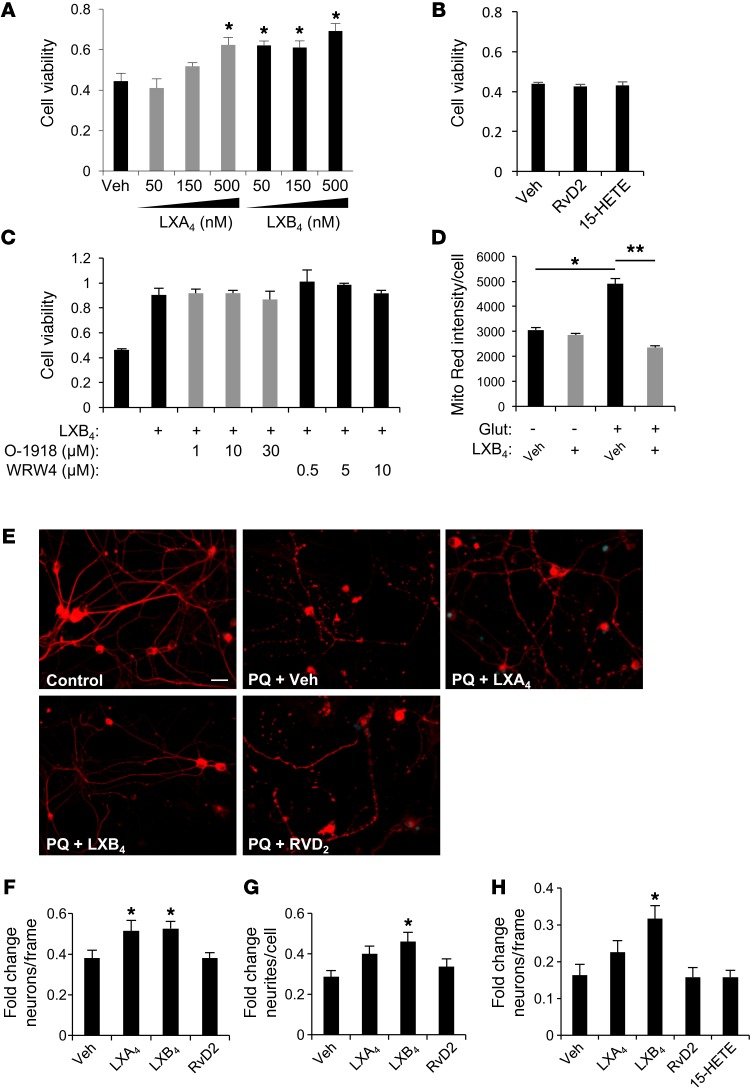
Figure 5. LXA4 and LXB4 have direct neuroprotective activities.
(A) Treatment of HT22 neuronal cells with LXA4 or LXB4 significantly protected them from metabolic insult in a dose-dependent manner up to 500 nM (n = 3). (B) No protective activity was observed by treatment with up to 1 μM of the related molecules 15-HETE or RvD2 (n = 3). (C) LXB4 protective activity at 500 nM was not blocked by treatment with increasing μM concentrations of WRW4 or the GPR18 antagonist O-1918 (n = 3). (D) MitoTracker red signal indicates protection from increased membrane potential with LXB4 treatment (n = 3) (E) Primary RGCs labeled with β3-tubulin extend an extensive network of neurites that disintegrate dramatically after 24 hours of 30 μM PQ. Intact neurites are significantly maintained by 1 μM LXB4, but not LXA4 or RvD2. (F) RGC survival following oxidative stress demonstrates significant rescue with treatment by LXA4 or LXB4 (n = 3). (G) RGC neurite degeneration following PQ challenge was significantly rescued by LXB4, but not LXA4 or RvD2 (n = 3). (H) Primary cortical neurons demonstrate a similar protective effect for LXB4 (n = 5). Scale bar: 20 μm. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Bars represent SEM. Statistical analyses were performed by 1-way ANOVA with TUKEY post-hoc test.