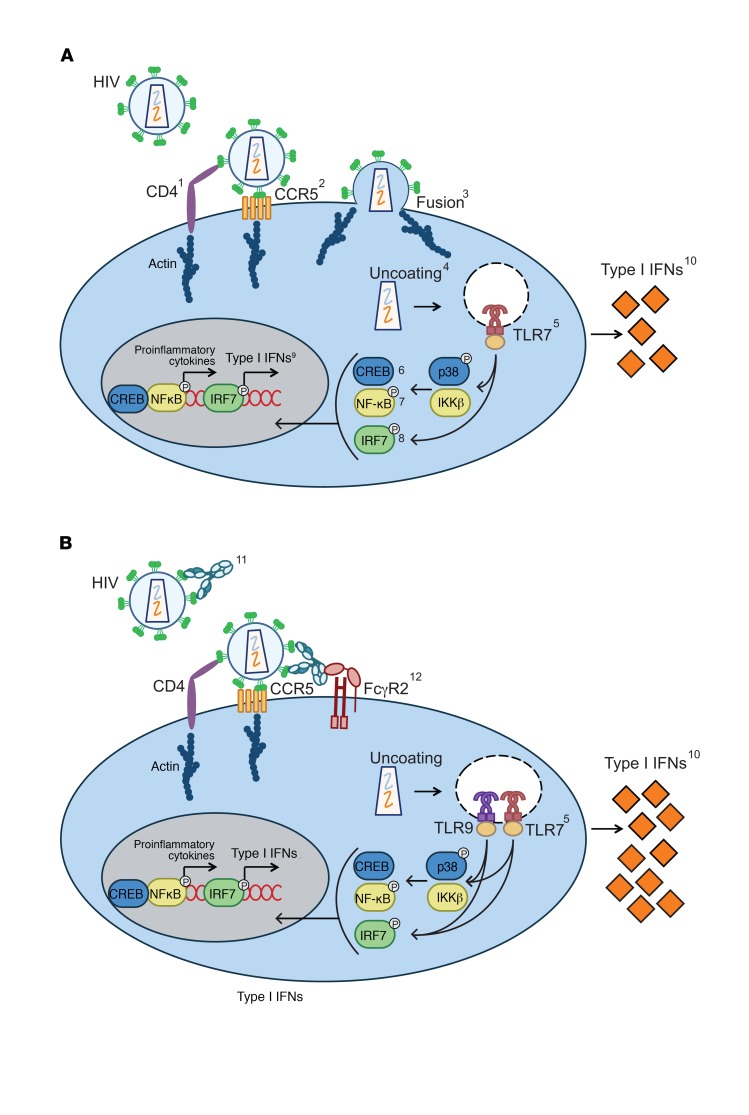
Figure 8. Suggested mechanism by which HIV-specific Abs that don’t block CD4 binding enhance type I IFN-s.
Representative diagrams of (A) IFN production by pDCs exposed to HIV and (B) enhanced IFN production by pDCs exposed to HIV preincubated with envelope-specific Abs that do not block CD4 binding. The 2 conditions diverge at 2 steps. First, the addition of Abs allows sensing of HIV without membrane fusion and through engagement of the FcγR2A; however, the engagement of both CD4 and CCR5 is still required. Secondly, in the presence of Ab, both endosomal TLRs, 7 and 9, sense the virus, while TLR9 plays no role in the absence of Ab. Inhibitors, Abs, and/or methods used to elucidate each step of the mechanism are listed here and numbered in the diagrams (A and B). Only steps of HIV sensing that differ when Ab is present are numbered in B. 1. anti-human CD4 Ab; 2. Maraviroc; 3. Enfuvirtide (T20); 4. CypA; 5. TLR 7 and TLR9 oligo inhibitors; 6. MAPK p38 inhibitor and Phosflow detection of phosphorylated p38; 7. IKKβ inhibitor and Phosflow detection of phosphorylated NF-kB p65; 8. Phosflow detection of p-IRF7; 9. Quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR (RTqPCR) detection of type I IFN mRNA; 10. ELISA detection of type I IFN protein. The following are shown in B only: 11. gp120 and gp41 mAbs and polyclonal IgG; 12. VRC01 variants, deglycosylated Abs, and FcR2-blocking Abs.