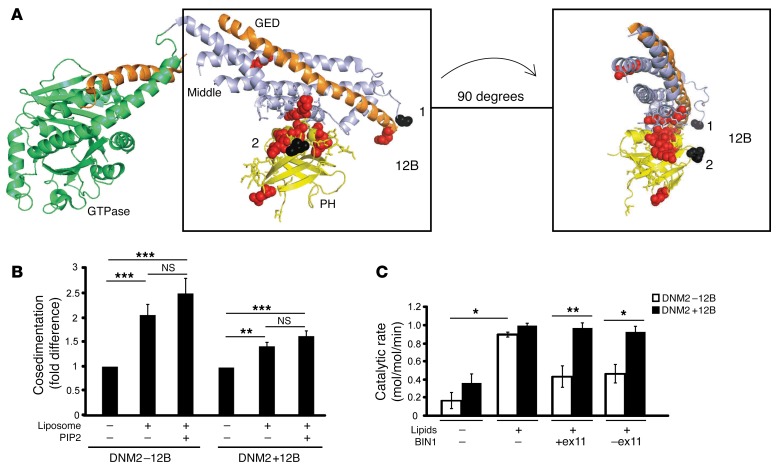
Figure 5. BIN1 inhibits DNM2 in an isoform-dependent manner.
(A) Crystal structure model of nucleotide-free human dynamin 1 (adapted from Faeber et al., ref. 52) using PyMOL. The GTPase domain (green), middle domain (light blue), and GTPase effector domain (GED, orange) forming the stalk, and the PH domain (yellow), are depicted, with the sites of DNM2 mutations linked to CNM indicated (red). The peptide encoded by 12B in human (CYYTEQLVTC) spans from position 497 (black 1), followed by 18 unresolved amino acids, and then amino acid 518 (black 2). (B) Cosedimentation assays were performed with recombinant proteins to determine protein binding (in pellet fraction) relative to total protein (pellet+soluble, see Supplemental Figure 7 for raw data), in the presence of liposomes and PIP2. Results are represented as a fold difference versus DNM2 alone. (C) Malachite green assay with DNM2 (±12B) and BIN1 (+exon 11 [Iso8] and –exon 11 [Iso9]) isoforms, with DNM2/BIN1 at a ratio of 1:4. Brain polar lipids with additional 5% PIP2 were used. Results are shown as catalytic rate (mol/mol/min). Results in B and C are an average of 2 (C) or 4 (B) independent experiments. Graph represents the mean + SEM. One-way (B and C) or 2-way (C) ANOVA test was used as described in the Methods section. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.