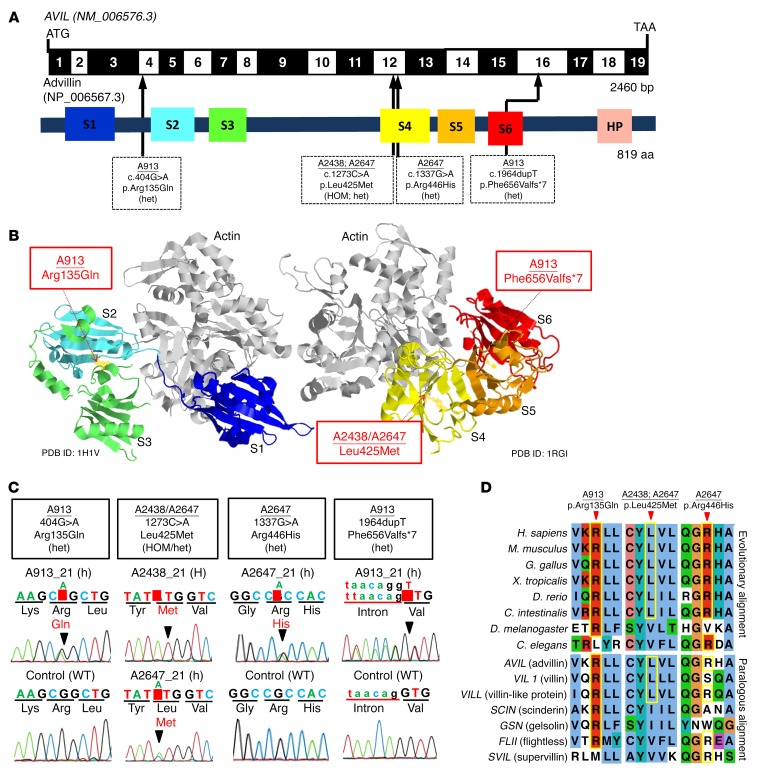
Figure 2. WES identifies recessive mutations of AVIL in 3 families with SRNS.
(A) Exon structure and functional domains of human AVIL cDNA. Positions of the start codon (ATG) and the stop codon (TAA) are indicated. Exons are marked on a black or white background. The length of protein domains is indicated by colored boxes. The positions of mutations (family numbers are underlined) are lined up by black arrows in relation to exons and protein domains (see also Table 1). (B) Ribbon diagram of the atomic structure of advillin. The gelsolin domains labeled S1 to S6 are color-coded blue (S1), aqua (S2), green (S3), yellow (S4), orange (S5), and red (S6), with actin shown in gray (Protein Data Bank [PDB] references: 1H1V and 1RGI). (C) Chromatograms of AVIL variants identified in individuals with SRNS. Sequence traces are shown for the variants above normal controls. Arrowheads denote altered nucleotides. (D) Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of AVIL throughout evolution and multiple sequence alignment of the human AVIL paralogs VIL1, VILL, SCIN, GSN, FLII, and SVIL using the Clustal_O program.