Fig. 7.
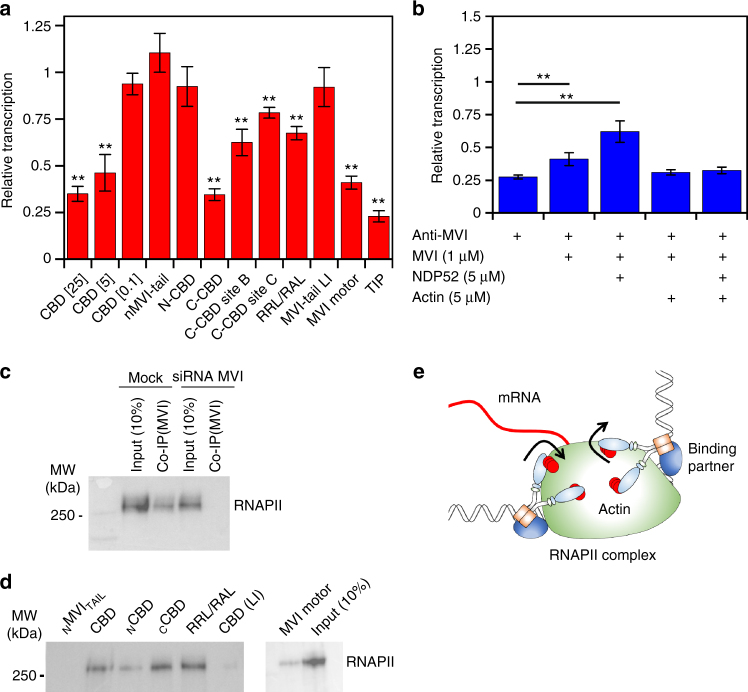
Coupling myosin VI to the RNAPII complex. a In vitro transcription by HelaScribe extracts in the presence of competitor MVI domains at 25 μM, unless stated otherwise. Sites B and C refer to CCBDΔSiteB and CCBDΔSiteC, respectively. TIP refers to the control reaction performed in the presence of 25 μM of the MVI inhibitor (TIP). Samples were normalised to the control sample in Fig. 6f (error bars represent SEM from five independent experiments **p < 0.001 by two-tailed t-test). See Supplementary Fig. 8c for control experiments. b In vitro transcription following antibody depletion and rescue using recombinant MVI (1 μM), NDP52 (5 μM) and F-actin (5 μM), as described in Methods (error bars represent SEM from five independent experiments **p < 0.001 by two-tailed t-test). c Co-immunoprecipitation of MVI and RNAPII, using an antibody against MVI to immunoprecipitate RNAPII from HeLa cells. Immunoprecipitation does not occur in HeLa cells subjected to siRNA knockdown of MVI. d Western blot against RNAPII following isolation from nuclear extracts by MVI constructs. Loading controls for the recombinant proteins is shown in Supplementary Fig. 9. e Working model of MVI in transcription elongation. MVI is bound to partner and/or DNA at the C terminus and RNAPII through actin at the N terminus