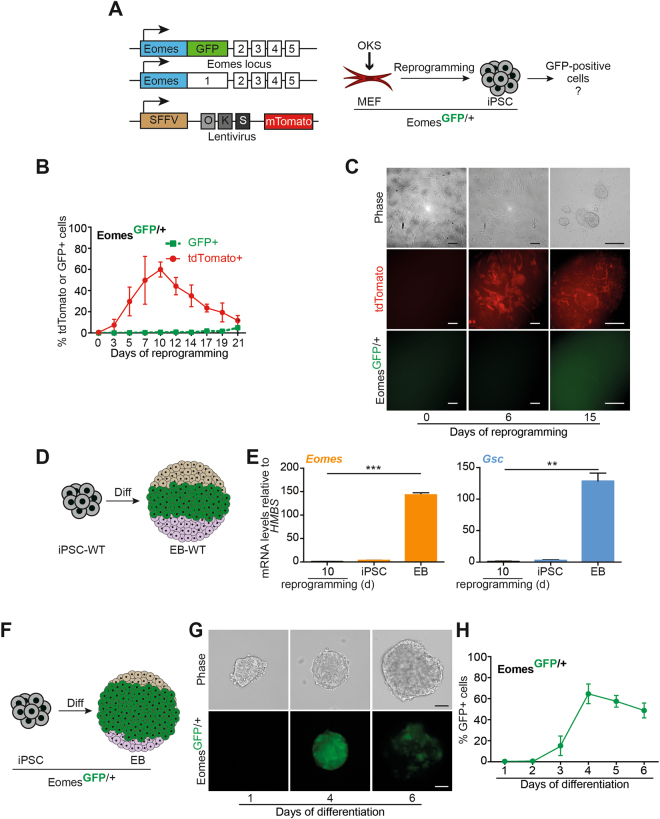
Figure 2.
EOMES protein is not detectable during several stages of murine fibroblast reprogramming. (A) Schematic illustration of the Eomes alleles used in (B–H). MEFs carry a GFP knock-in at the Eomes GFP/+ locus (upper and middle panel) allowing for quantification of Eomes GFP/+ positive cells by putative GFP expression19. A lentiviral 3-factor (OKS) reprogramming construct includes a tdTomato reporter to track expression of pluripotency markers during reprograming20. (B) FACS-based quantification of GFP- and tdTomato-positive cells during reprogramming at the indicated days. GFP-positive cells arise only late, after the reprogramming process indicating differentiation of formed iPSCs (day 21). (C) Corresponding phase contrast images (upper panel) and fluorescence images of the MEF cultures during reprogramming (red, middel panel) and the Eomes GFP/+ reporter signal (green, lower panel). (D) Scheme for spontaneous in vitro differentiation of WT-iPSCs towards embryoid bodies representing early germ layer formation mirrored in the three colors. (E) Comparison of marker gene expression for mesendoderm expression peaks during reprogramming of murine fibroblasts in comparison to iPSCs and cells differentiated in EBs. All mRNA levels are expressed relative to the housekeeping gene Hmbs and values have been normalized to day 10 reprogramming cultures, which have been set to 1 to illustrate fold induction. (F) Scheme for in vitro differentiation of Eomes GFP/+ reporter iPSCs isolated from (A) in embryoid bodies toward mesendoderm using high doses of Activin A. Germ layer formation is mirrored in the three colors, while high doses of Activin A favor endoderm formation (green). (G) Eomes GFP/+ reporter iPSCs are differentiated towards mesendoderm. Expression of GFP validates the functionality of the Eomes GFP/+ reporter. (H) FACS-based quantification of independent experiments from (G).