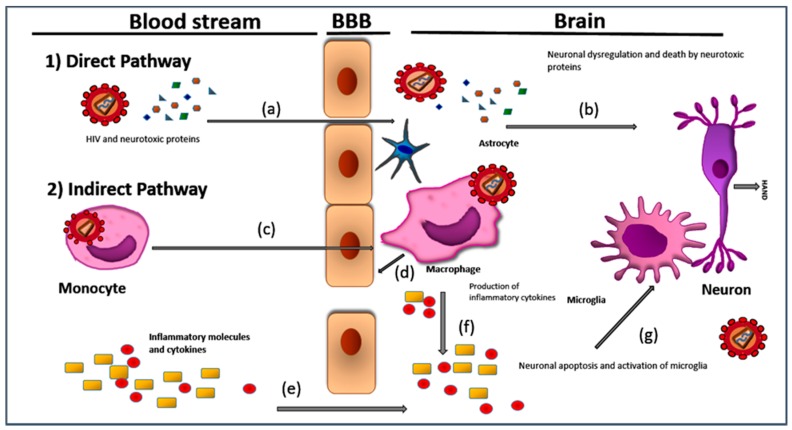
Figure 1.
Mechanism of neuropathogenesis. Two pathways involved shown by arrows: (1) Direct pathway caused by HIV and released HIV proteins. (2) Indirect pathway involving secretion cytokines. (a) Virus particles and viral proteins shed and cross Blood brain barrier (BBB). (b) Neural injury caused by direct viral infection and dysregulation by viral proteins. (c) Infected monocyte infiltrating BBB. (d) Release of cytokines from infected monocytes contributing to disruption of BBB. (e) BBB become more permeable to cytokines present in the periphery. (f) More cytokines released into the brain and (g) cytokines disrupt normal functioning ultimately leading to neuronal apoptosis resulting in different forms of HIV associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND).