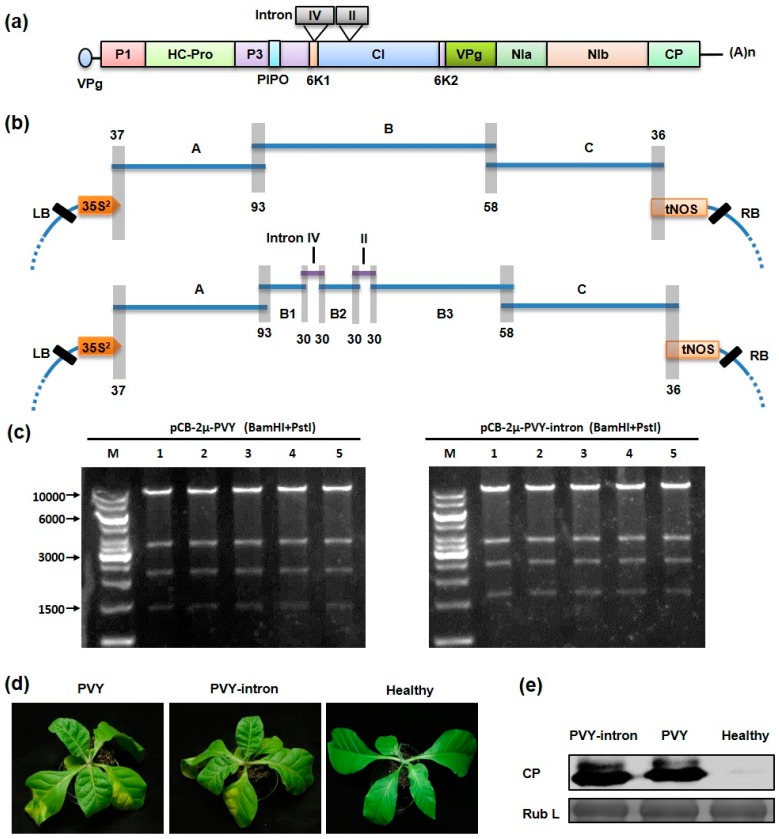
Figure 3.
One-step assembly of intron-less and intron-containing potato virus Y (PVY) infectious cDNA clones by homologous recombination in yeast: (a) PVY genome structure. The 5’ viral protein genome-linked (vpg) and the 3′ polyadenylated tail [(A)n] are depicted. The positions of two inserted introns are indicated on the top of the genome; (b) Schematic representation of the cloning strategies for yeast homologous recombination-mediated assembly of the PVY intron-less (upper panel) and intron-containing (lower panel) full-length clones. The intron-less PVY clone was assembled by co-transformation of yeast cells with the three overlapping PVY cDNA fragments (A, 3311 bps; B, 3359 bps; C, 3259 bps) and the appropriately linearized vector pCB301-HDV-2μ. For the intron-containing clone, the B fragment is divided into three fragments (B1, B2 and B3) by insertion of the two inserted intron (IV and II). The overlapping regions are depicted by gray boxes, with the number of overlapping nucleotides indicated. Note that all of the fragments in the figure are not drawn exactly to scale; (c) Recombinant plasmids were digested with BamHI and PstI and the products were separated on 0.8% agarose gels. The positions of the 10,000, 6000, 3000 and 1500 bp size markers (M) are indicated to the left of the panel; (d) Nicotiana tabacum plants systemically infected with the intron-less or intron-containing PVY infectious clone were photographed at 15 days post infiltration. Healthy: an uninfected plant; (e) Total proteins extracted from PVY infected plants were analyzed by Western blotting using an antibody against the PVY CP protein. The Coomassie blue-stained Rubisco large subunit (Rub L) is used as a loading control.