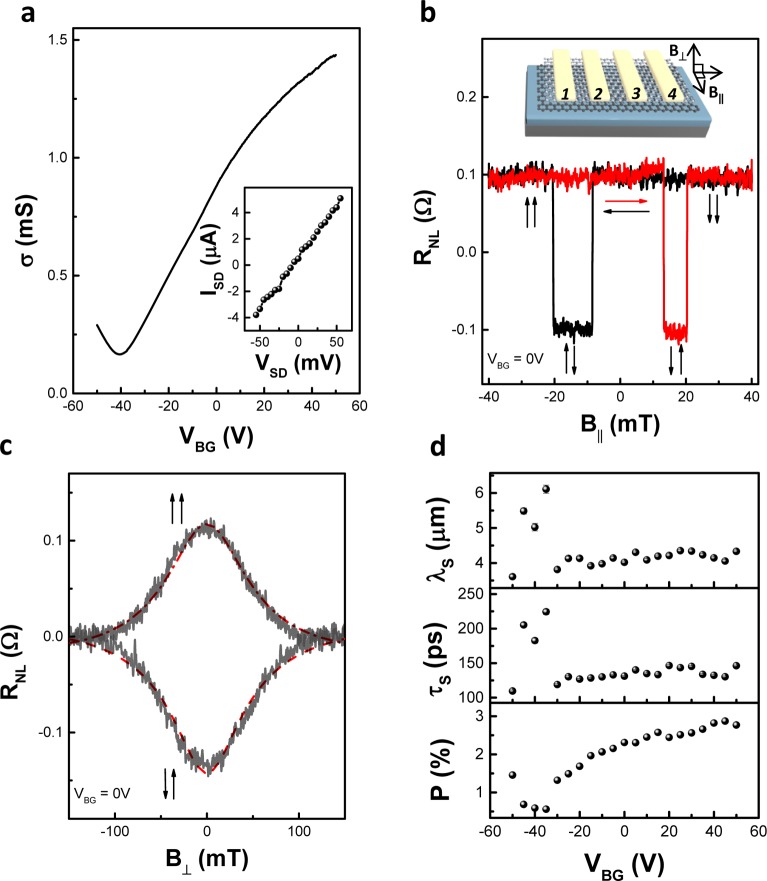
Figure 2.
Electrical characterization of the graphene spin valve with a h-BN tunnel barrier. (a) Back-gate voltage dependence of graphene conductivity. Inset shows the I–V dependence of injector and detector electrodes. They are labeled 2 and 3, respectively in the schematics shown in the inset of panel b. (b) Nonlocal signal as a function of in-plane magnetic field. Black and red horizontal arrows represent the magnetic field sweeping directions. Vertical arrows represent the relative magnetization directions of the injector and detector electrodes. Inset: Schematics for nonlocal spin transport measurement. A charge current of 5 μA is applied from electrode 1 to 2, and the generated spin current is detected by probing the electrochemical potential differences between electrodes 3 and 4. (c) Hanle precession of the nonlocal signal as a function of the perpendicularly applied magnetic field. Measurements are performed at VBG = 0 V. (d) Back-gate voltage dependence of spin relaxation length, spin relaxation time, and spin injection efficiency.