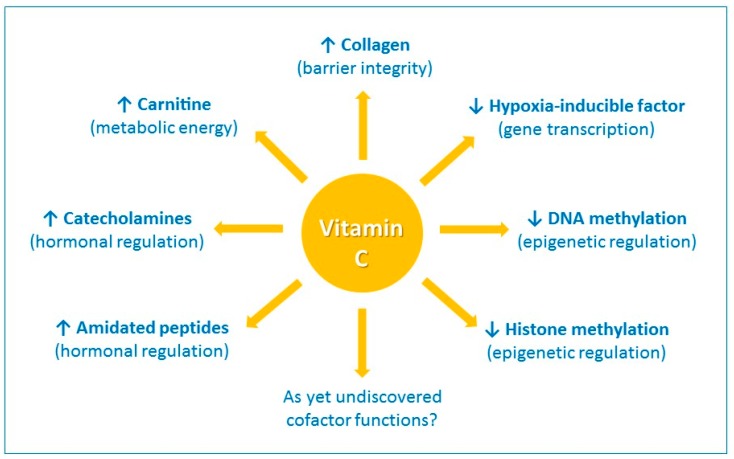
Figure 1.
The enzyme cofactor activities of vitamin C. Vitamin C is a cofactor of a family of biosynthetic and gene regulatory monooxygenase and dioxygenase enzymes. These enzymes are involved in the synthesis of collagen, carnitine, catecholamine hormones, e.g., norepinephrine, and amidated peptide hormones, e.g., vasopressin. These enzymes also hydroxylate transcription factors, e.g., hypoxia-inducible factor 1α, and methylated DNA and histones, thus playing a role in gene transcription and epigenetic regulation. ↑ indicates an increase and ↓ indicates a decrease.