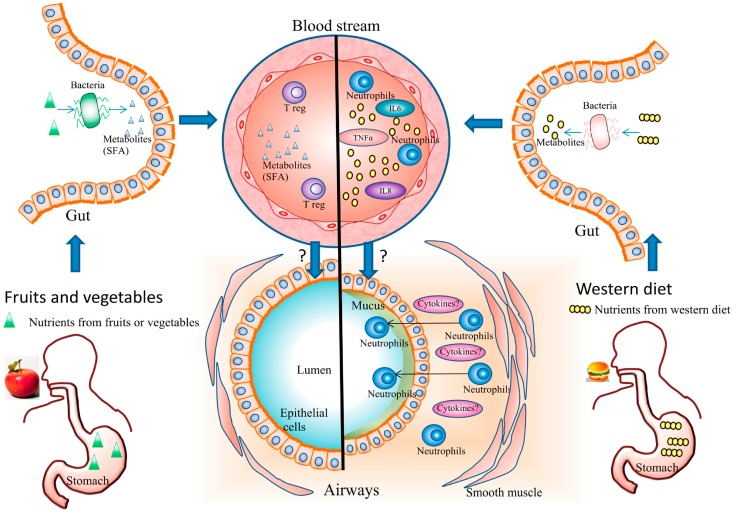
Figure 2.
Systemic and airway effects of dietary patterns on asthma. The Western diet promotes a pro-inflammatory environment and causes an increase in airway inflammation. Fruit and vegetable consumption has systemic anti-inflammatory properties, with a decrease of pro-inflammatory cytokines in plasma. Fruit and vegetables are also associated with lower airway inflammation and a reduction of neutrophils in asthmatics. Gut microbiota plays a role in immune response to diet in asthma. Metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) (including ω-3 fatty acids) that have immunomodulatory effects are produced in high amounts after fruit and vegetable intake. The western diet altered microbiota composition and potentiate inflammation.