Figure 1.
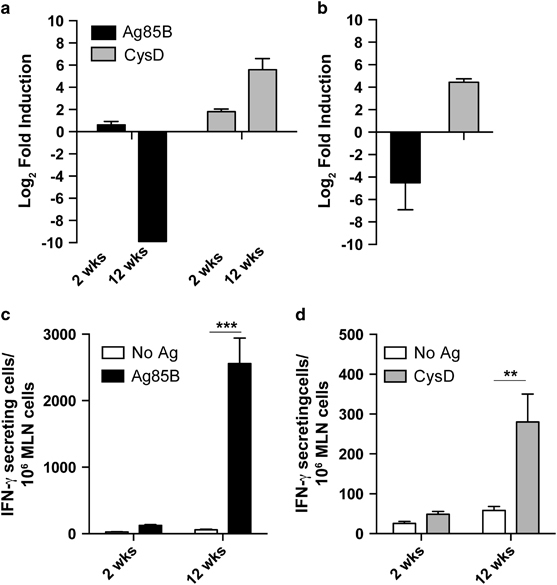
Pulmonary induction of the M. tuberculosis cysD gene during chronic infection of mice. C57BL/6 mice (n=4–5) were infected with ~100 CFU of M. tuberculosis H37Rv by aerosol route. Transcript levels of either fbpB and cysD were determined by quantitative real-time PCR from M. tuberculosis RNA isolated from the lung of mice at 2 and 12 weeks post-infection (a) or from DETA-NO-exposed in vitro M. tuberculosis cultures (b). Data are presented as relative expression of the genes compared with exponential phase in vitro-grown M. tuberculosis and normalised to the expression of the 16S rRNA gene. The IFN-γ response of MLN cells to Ag85B (c) or CysD (d) was determined by ELISPOT at 2 and 12 weeks post-infection and compared with unstimulated cells. Data are presented as IFN-γ producing cells per million cells±s.e.m., and are representative of two independent experiments. The significance of differences between groups was determined by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (*P<0.05; **P<0.01).
