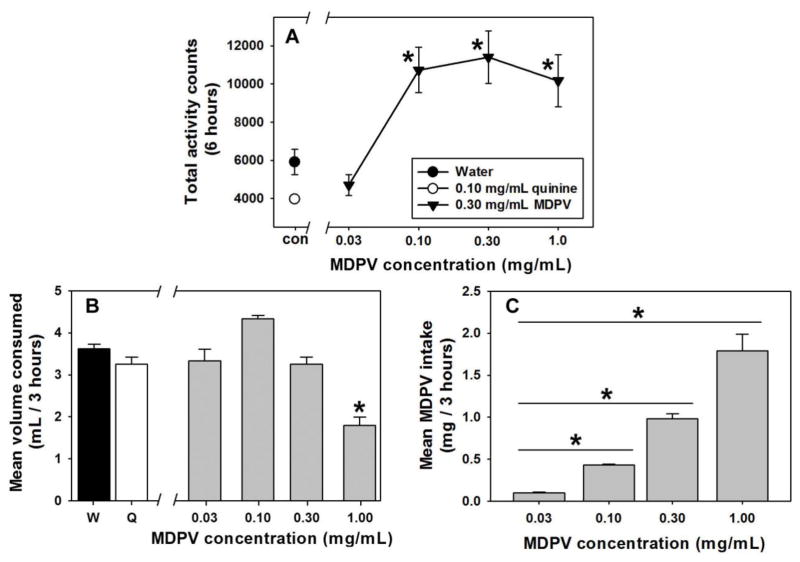
Figure 2.
A – Locomotor effects of water (filled circle), 0.10 mg/mL quinine solution (open circle) or MDPV solutions (filled triangles) in a forced choice setting after 21-hours of fluid restriction. Abscissa: Fluid available, with water and quinine control solutions presented at the “con” point, and with MDPV concentrations expressed as mg/mL on a log scale. Ordinate: Total locomotor counts summed over 6 hours during and after 3 hour access to each fluid. Asterisks represent significant differences from water control. B – Effects of water (filled bar), 0.10 mg/mL quinine solution (open bar), and each concentration of MDPV solution (gray bars) on fluid consumption during locomotor activity assessments. Abscissa: Fluid available, with water and quinine control solutions presented at the “W” and “Q” points, respectively, and with MDPV concentrations expressed as mg/mL on a log scale. Ordinate: Total volume consumed in mL during the 3 hour access period. Asterisk represents significant difference from water control. C – MDPV intake as a function of concentration of available MDPV solutions. Abscissa: MDPV concentrations expressed as mg/mL on a log scale. Ordinate: Total intake of MDPV, expressed as mg/3 hours. Asterisks indicate significant differences from lower MDPV concentrations.