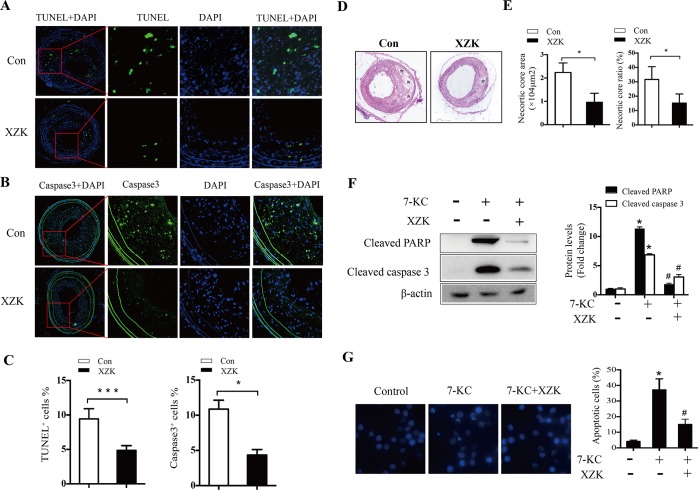
Fig 3. Effect of XZK on macrophage apoptosis.
(A-B) Representative images of apoptotic cells in lesions from ApoE-/- control and XZK-treated mice as determined by TUNEL assay (A) and immunofluorescence staining of cleaved caspase-3 (B). (C) Quantification of TUNEL+ (left) and cleaved caspase-3+ (right) cells (n = 4–5 animals per group). (D-E) H&E staining in lesions from ApoE-/- control and XZK-treated mice (*, necrotic areas) (D) and quantification of necrotic core area (E, left) and ratio (E, right) (n = 5 animals per group). (F) RAW264.7 cells were treated with 7-KC (70 μM) in the absence or presence of XZK (100 μg/ml) for 16 h. PARP and caspase-3 cleavage were analyzed by immunoblotting (n = 3). (G) RAW264.7 cells were treated with 7-KC (70 μM) in the absence or presence of XZK (100 μg/ml) for 16 h. Nuclear morphology was examined by DAPI staining (left) and the number of apoptotic cells was quantitated (n = 5). *P < 0.05 or ***P < 0.001 versus control; #P < 0.05 versus 7-KC-treated along. Abbreviations: XZK, Xuezhikang; DAPI, 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; 7-KC, 7-ketocholesterol.