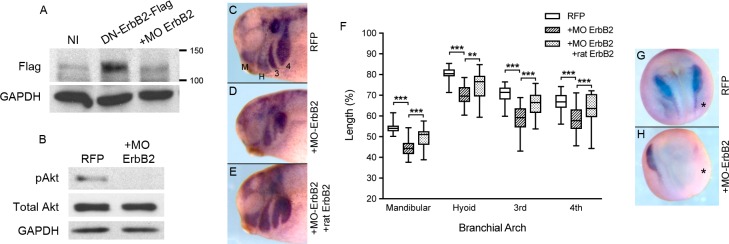
Fig 6. Knockdown of ErbB2 decreases phosphorylation of Akt and CNC migration.
(A) Western blot of non-injected (NI) and injected embryo extracts probed for flag. Single-cell embryos were injected with 800 pg DN-ErbB2-Flag mRNA with or without 25 ng of ErbB2 morpholino (MO ErbB2). Translation of DN-ErbB2-flag was hindered in embryos co-injected with MO ErbB2. GAPDH is shown as a loading control. One-embryo equivalents are loaded per lane. (B) Western blot of CNC extracts probed for phospho-Akt, total Akt and GAPDH. Eight-cell embryos were either injected with 200 pg RFP mRNA alone (N = 4, n = 32) or with 3.1 ng MO Erb2 (N = 3, n = 43) into CNC progenitor cells. CNC cells were then dissected from embryos once they reached stage 17–18. Injection of MO ErbB2 into CNC cells precursors dramatically reduced phosphorylation of Akt without altering the levels of control proteins. Ten CNC explants are loaded in each lane. (C-E) Early tailbud stage embryos labeled for Twist and Sox10 CNC markers using in situ hybridization. Embryos were injected as in part (B) along with a set injected with 300 pg rat ErbB2-flag and 1.6 ng MO ErbB2 (E; N = 2, n = 20). Embryos injected with RFP mRNA and MO ErbB2 showed defects in CNC migration (D) compared to RFP-injected controls (C). Migration was partially rescued by co-injecting the morpholino with rat ErbB2-flag mRNA (E). (F) CNC migration was measured in each branchial arch and normalized to head size from embryos in part (C-E). Co-injection of MO ErbB2 with RFP mRNA significantly reduced CNC migration in the mandibular (M), hyoid (H), 3rd and 4th branchial arches. Co-injection of MO ErbB2 with rat ErbB2 mRNA partially rescued migration. Error bars are one standard deviation to the mean. One-tailed, Student’s t-tests were performed to determine statistical significance. ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. N, number of experiments; n, number of embryos.