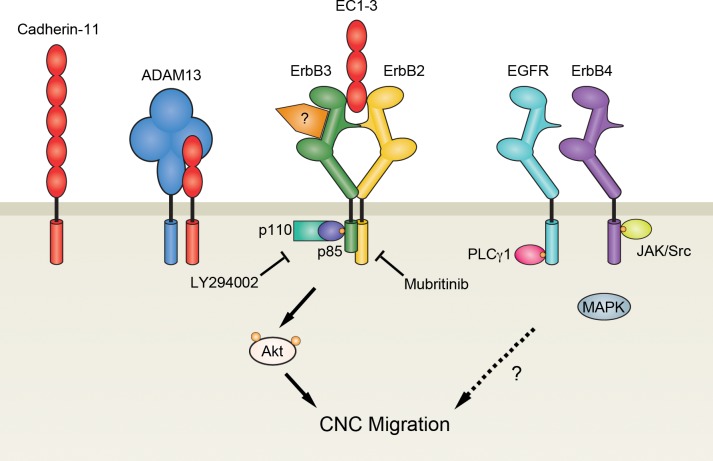
Fig 8. EC1-3 stimulates Akt and CNC migration.
During migration of cranial neural crest (CNC) cells, ADAM13 (blue) cleaves the extracellular domain of cadherin-11 (red) at the cell surface to release a soluble fragment (EC1-3) capable of promoting CNC migration. EC1-3 can induce cell migration by binding to ErbB receptors: EGFR/ErbB1 (teal), ErbB2 (yellow), ErbB3 (green) and ErbB4 (purple). In particular, binding of EC1-3 with ErbB2-ErbB3 dimers increases docking of the regulatory (p85) subunits of PI3K. Recruitment of PI3K to the cell membrane ultimately leads to the phosphorylation of Akt, which is important for CNC migration. Because inhibition of ErbB2 is less detrimental to cell migration than inhibition of all ErbB receptors, it is possible that EC1-3 utilizes Akt-independent pathways downstream of ErbB dimers that do not include ErbB2. Whether EC1-3 signaling first requires receptors to bind their cognate ligand still needs to be investigated.