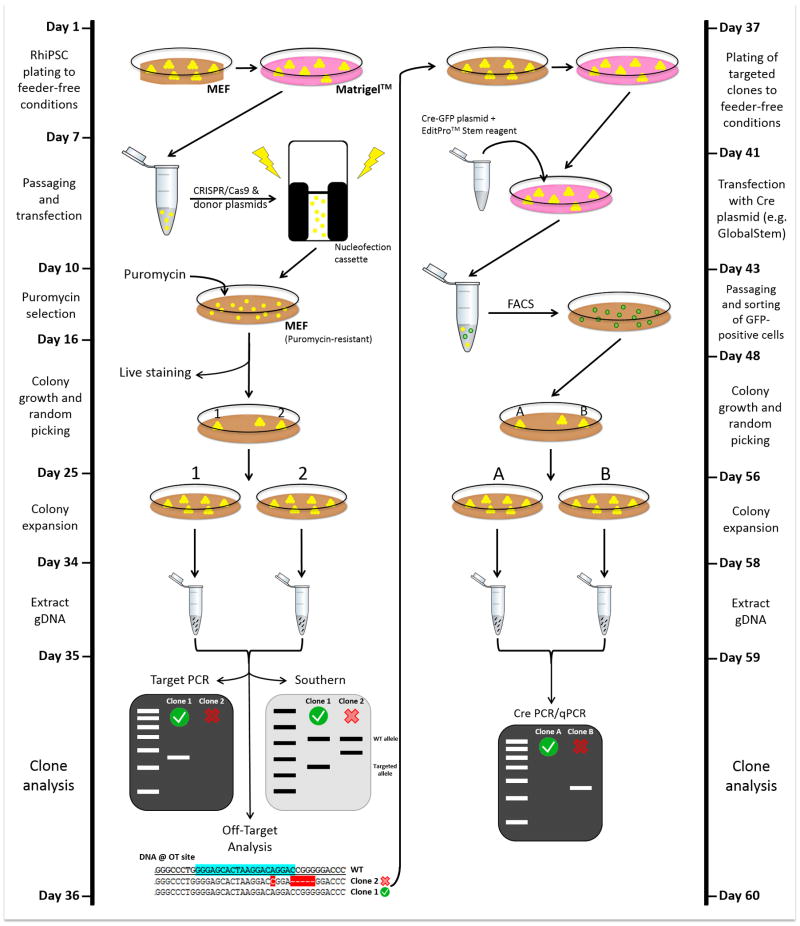
Figure 1.
Timeline and workflow for CRISPR/Cas9-based safe-harbor gene editing in RhiPSCs.
RhiPSCs in feeder-free condition are harvested. A donor plasmid and the CRISPR/Cas9 “all-in-one” vector are delivered to RhiPSCs via nucleofection. The donor plasmid described in this protocol allows puromycin-mediated selection to enrich cells that have targeted insertion at the desired AAVS1 locus. Optionally, live-cell staining with the antibody against the transgene in the donor plasmid can be performed to make the colony selection process easier. After targeting, colonies need to be screened by PCR, Southern blot, and off-target analyses. Examples of a correct clone (clone #1) and a non-desirable clone (clone #2) for each assay is shown. Clones that have targeted insertion in one or both alleles (monoallelic or biallelic) with no additional random integration or off-target mutation should be selected for further steps. Right panel depicts additional subcloning step to remove the puromycin resistance gene. In this case, RhiPSCs are transfected with the GFP-Cre plasmid and positive cells are purified by FACS. Of note, GFP reporter in sorted cells is transient, hence will be lost by the time of colony growth and picking as illustrated on Day 48. Excised clones are confirmed by Cre PCR/qPCR. An example of a correctly excised clone (Clone A) and partial/non-excised clone (Clone B) is shown.