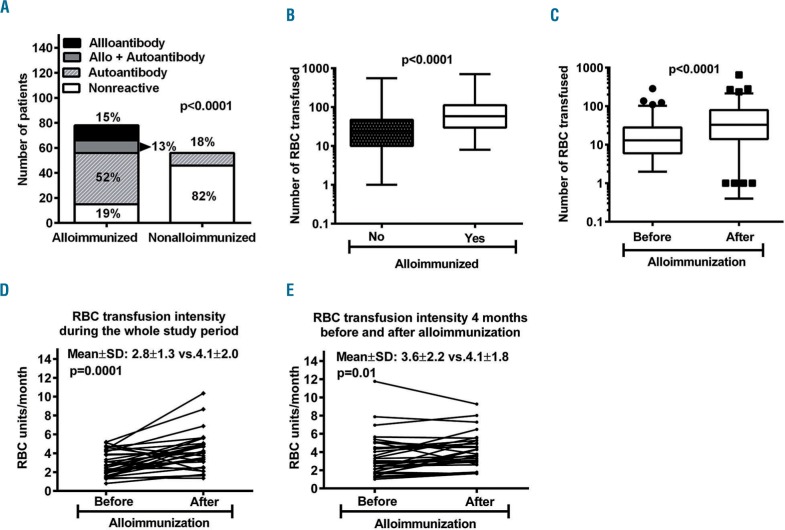
Figure 2.
Alloimmunization is associated with autoantibody formation and increased red blood cell transfusion requirement. (A) Autoantibodies were detected in a significantly higher number of alloimmunized patients than in non-alloimmunized ones (65% vs. 18%; P<0.0001) (B) The total number of RBC units transfused was significantly higher in alloimmunized patients than in non-alloimmunized patients (P<0.0001) (C) In alloimmunized patients, the total number of RBC units transfused was significantly higher after alloimmunization (D) RBC transfusion intensity was significantly higher following alloimmunization during the whole study period (E) RBC transfusion intensity compared over 8 months (4 months before and 4 months after alloimmunization) also confirmed that RBC transfusion intensity increases significantly following alloimmunization.