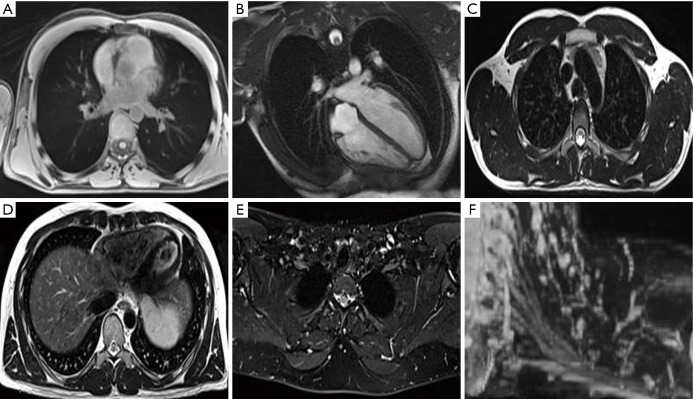
Figure 3.
MRI of OARs for treatment planning. MRI of a normal volunteer: (A) axial T1 radial 3D spoiled gradient echo sequence (GRE) in free breathing for visualisation of proximal tree bifurcations, heart, great vessels, spinal cord and lungs; (B) heart long axis balanced steady state free precession (cardiac gated) for visualisation of the heart and cardiac chambers; (C) axial T2 Turbo Spin Echo (TSE) with no fat saturation (respiratory triggered to exhale) for visualisation of great vessels, oesophagus and spinal cord; (D) axial T2 TSE with no fat saturation (respiratory triggered to exhale) for visualisation of the pericardium, heart and liver boundary; (E) axial Dixon TSE, water image reconstruction for visualisation of the brachial plexus; (F) coronal MIP of axially acquired DIXON TSE for visualisation of the brachial plexus. MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; OARs, organ at risks; MIP, maximum intensity projection.