Figure 1.
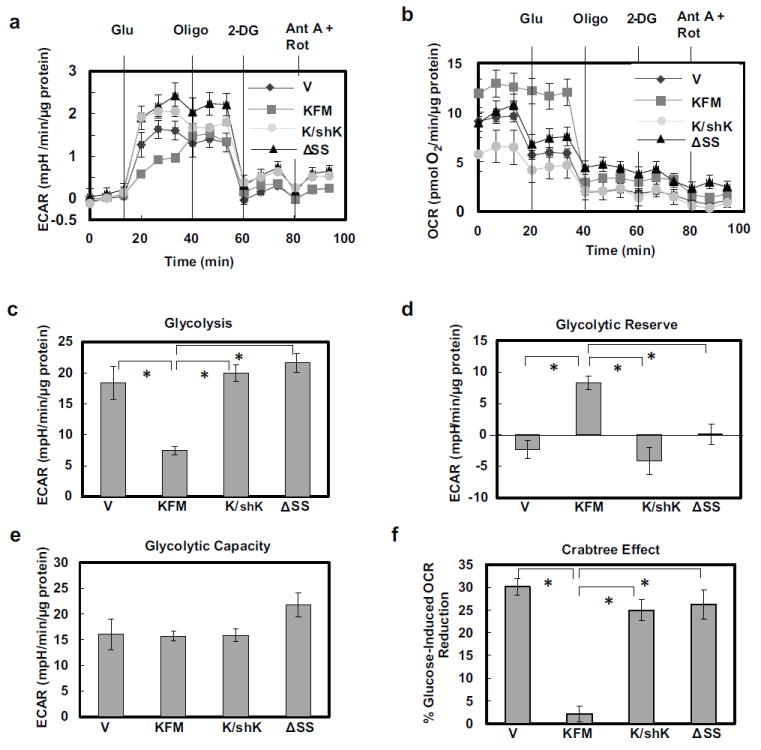
KISS1 inhibits both glycolysis and the Crabtree effect. A Seahorse XF24 bioanalyzer was used to measure extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) (a) and mitochondrial oxygen consumption rate (OCR)(b) in C1861.9Vector (V), C8161.9KFM59(KFM), C8161.9KFM59/shKISS1 (K/shK), and C8161.9KFMΔSS6 (ΔSS) cells under basal conditions followed by sequential injections of 10 mM glucose (Glu), 1 μM oligomycin (Oligo), 50 mM 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG), and 2 μM antimycin A (Ant A) and 4 μM rotenone (Rot). Basal glycolysis (c), glycolytic reserve (d), and glycolytic capacity (e) are derived from ECAR measurements in (a). Crabtree effect (f) is derived from OCR measurements in (B). N = 5; error bars, SEM; * P ,< 0.05
