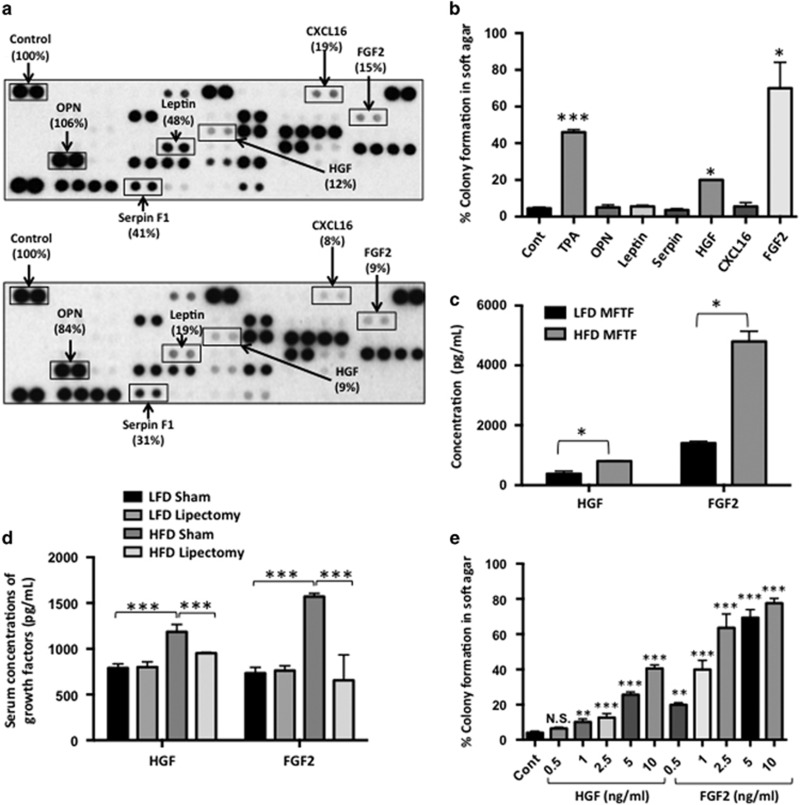
Figure 2.
Lipectomy reduces transformation-stimulating serum growth factors in HFD-fed mice. (a) SKH-1 mice were fed either a HFD or LFD for 2 weeks, and half the mice had their parametrial adipose tissue removed or received a sham operation (n=20/group). After 33 weeks of UVB exposure, serum was isolated. Protein Profiler angiogenesis array of pooled sera of HFD-fed sham-operated mice (top panel) and HFD-fed lipectomized mice (bottom panel). HFD-fed mice that had the surgical removal of parametrial adipose tissue showed a decrease in several pro-inflammatory proteins in the circulation. Boxed proteins were those found to be both reduced with lipectomy and induced in the MFTF with HFD (Figure 1d). Dot intensity was analyzed by ‘ImageJ’ software. Data are labeled as the percent of the control (reference) dots located in the upper left hand corner of the arrays. (b) Proteins found in a were tested for their transforming activity in the soft agar assay. HGF (10 ng/ml) and FGF2 (10 ng/ml) significantly stimulated colony formation in soft agar. 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA, 10 ng/ml) was used as a positive control. (c) HGF and FGF2 levels in MFTF from Figures 1a and d were quantified by ELISA. HFD feeding increases the levels of both HGF and FGF2. (d) SKH-1 mice were treated as described in a. Serum was isolated and analyzed for HGF and FGF2 by ELISA. (e) Dose response of HGF and FGF2 on JB6 P+ cell transformation. Data are presented as mean±s.d. of values from triplicates and statistical significance was determined using a one-way ANOVA (b–e) followed by a Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons (d) (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001).