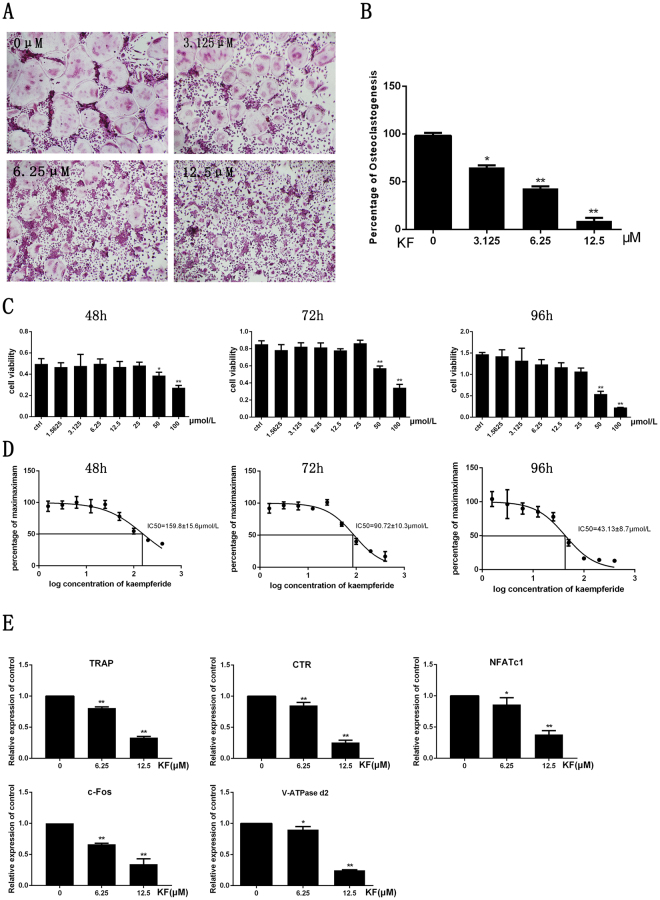
Figure 1.
KF inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation in vitro. (A) BMMs were treated with various concentrations of KF followed by 30 ng/ml M-CSF and 50 ng/ml RANKL, after incubation for 7 days, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and subjected to TRAP staining. (B) Number of TRAP-positive multinucleated osteoclasts. (C) KF shows no cytotoxicity at low concentrations. Viability of KF treated BMM cells after being incubated for 48 h, 72 h and 96 h. (D) The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of kaempferide was 159.8 ± 15.6 μM, 90.72 ± 10.3 μM and 43.13 ± 8.7 μM, respectively. (E) KF suppresses RANKL-induced gene expression. BMM cells were cultured with M-CSF (30 ng/ml), RANKL (50 ng/ml) and KF (6.25 μM and 12.5 μM) for 5 days. RANKL-inducible gene expression was analyzed by real time PCR. RNA levels were normalized relative to the expression of Beta-actin (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).