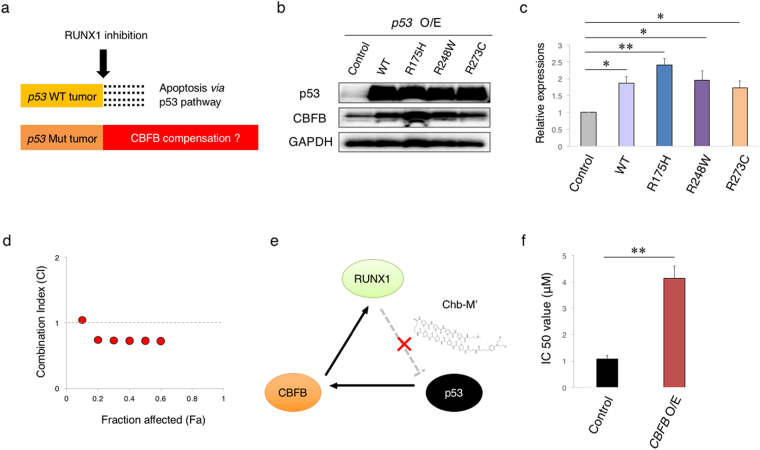
Figure 4.
Mutated p53 induces CBFB. (a) Schematic abstract showing the different biological response to RUNX1 inhibition of p53-proficient and p53-mutated tumors. (b) p53 mutants induce the expression of CBFB. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated expression plasmids. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (c) Cumulative results of (a). Signal intensities of the bands for CBFB were measured by Image Lab software and adjusted to those of GAPDH bands. Values were normalized to that of control samples (n = 3). (d) Combination index plots of Ro5-3335 and CP-31398 in p53-mutated (MV4-11NR) AML cells (n = 3). (e) Schematic illustration showing the interaction site of Chb-M’ in the RUNX1-p53-CBFB loop. Chb-M’ binds to RUNX1-consensus binding sequences on the genome DNA, inhibits the recruitment of RUNX1 onto its target sites, and thereby activating p53 pathway. (f) IC50 values of Chb-M’ in MV4-11 cells transduced with the empty lentivirus or with the lentivirus for CBFB (CBFB O/E). Cells were simultaneously treated with 3 μM of doxycycline and various concentrations of Chb-M’ for 48 hours (n = 3). Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, by two-tailed Student’s t-test.