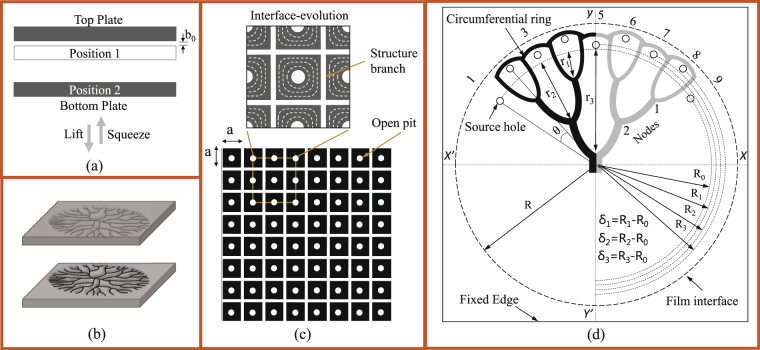
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of (a) Lifted Hele-Shaw cell with parallel separation wherein the bottom plate squeezes the fluid against a top fixed plate to a final thickness of b 0 and radius R (position 1). Separation of plates is carried out while maintaining parallelity between the two cell plates (position 2). (b) Isometric representation of Hele-Shaw cell and the type of branched pattern that evolves, in the absence of controlling source-hole, on both cell plates as mirror images of each other. (c) Layout of ports/source-holes on one of the cell plate for fabricating a regular square arrayed structure with each cell size a × a. Enlarged section shows evolution of the interface (uniform interaction among the fingers) in lifting process giving rise to ordered structure branches. (d) Layout of source-holes on a cell plate and the type of controlled Cayley tree structure that would evolve from such a layout. Source-holes are placed at a radius of from the center wherein with all the source-holes equally apart from each other by an angle θ. The inner most source-holes are at a radius of R 0 and the radius to which the fluid film interface is stretched is R. Non-uniformity (waveness) in circumferential ring is an exaggeration, of actually near-circular ring formed, so as to represent the source-hole positions at different . In experiments, magnitude of δ n nedeed to shape the fluid into a tree-like pattern is very small (~μm).