FIG 3.
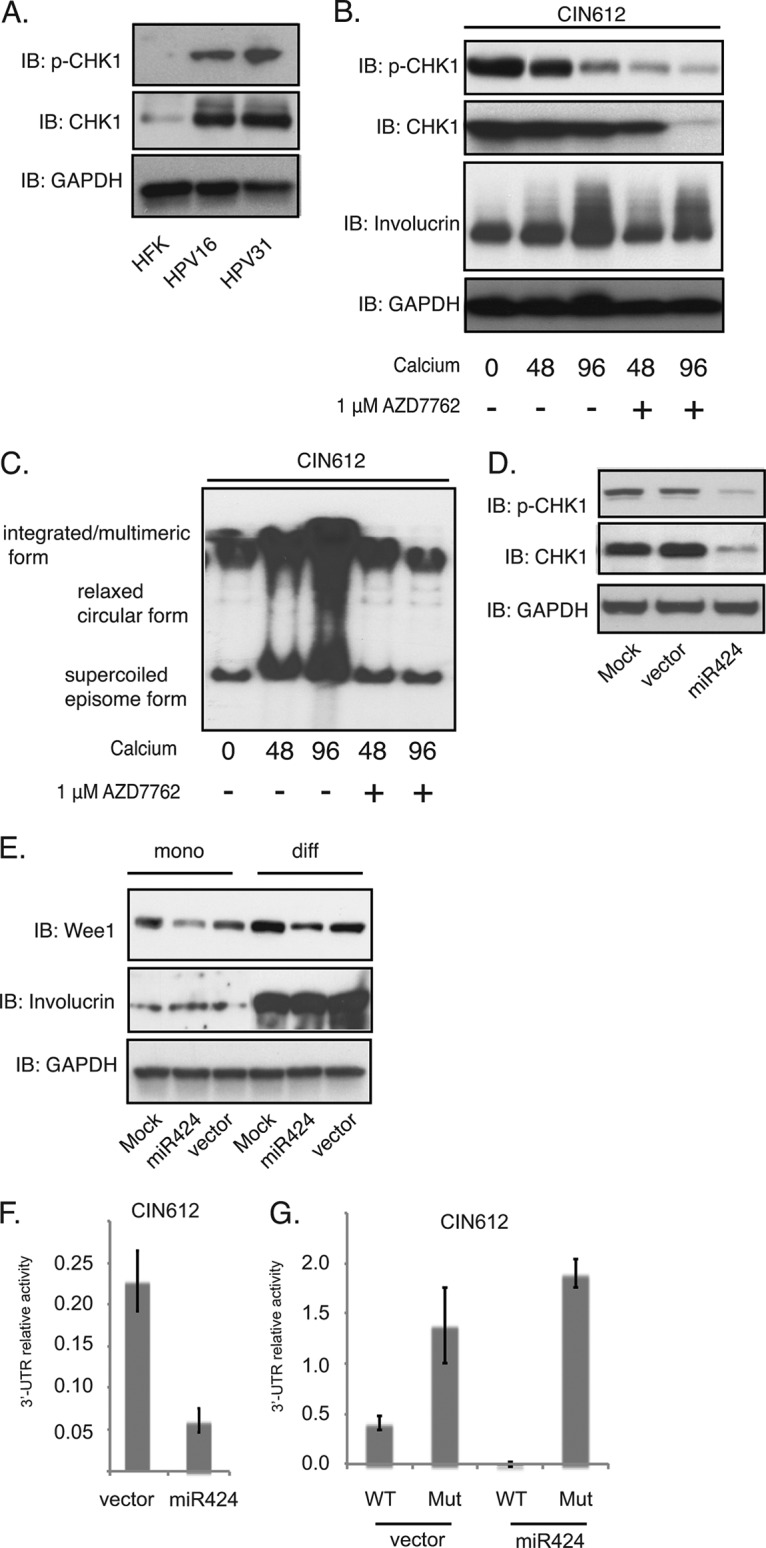
CHK1 is a miR-424 downstream target and is necessary for HPV31 genome amplification. (A) Western blot analysis of p-CHK1, CHK1, and GAPDH proteins in HFKs and in HPV16- and HPV31-positive cells. (B) Western blot analysis of p-CHK1, CHK1, involucrin, and GAPDH proteins in CIN612 cells in the presence or absence of AZD7762 (1 μM) after differentiation in high-calcium media for the indicated times. (C) Southern blot analysis for HPV31 episomes in CIN612 cells after AZD7762 treatment and differentiation in high-calcium media for the indicated times (in hours). (D) Western blot analysis of p-CHK1, CHK1, and GAPDH proteins in CIN612 cells stably expressing either vector alone or miR-424. (E) Western blot analysis of Wee1, involucrin, and GAPDH proteins in undifferentiated or differentiated (“mono” versus “diff”) CIN612 cells stably expressing either vector alone or miR-424. (F) The luciferase reporter vector containing wild-type CHK1 3′ UTR was transfected into CIN612 cells stably expressing either vector alone or miR-424. The firefly luciferase activities were determined 48 h after transfection and normalized to Renilla luciferase. The relative luciferase activities were normalized to the control pmiRGLO plasmid. Each column stands for the mean value plus the standard deviation of three independent experiments. (G) The luciferase reporter vector containing wild-type CHK1 3′ UTR or a mutant CHK1 3′ UTR was transfected into CIN612 cells transduced with miR424-expressing lentiviruses. The luciferase activities were determined as in panel F. All results are representative of observations from three independent experiments.
