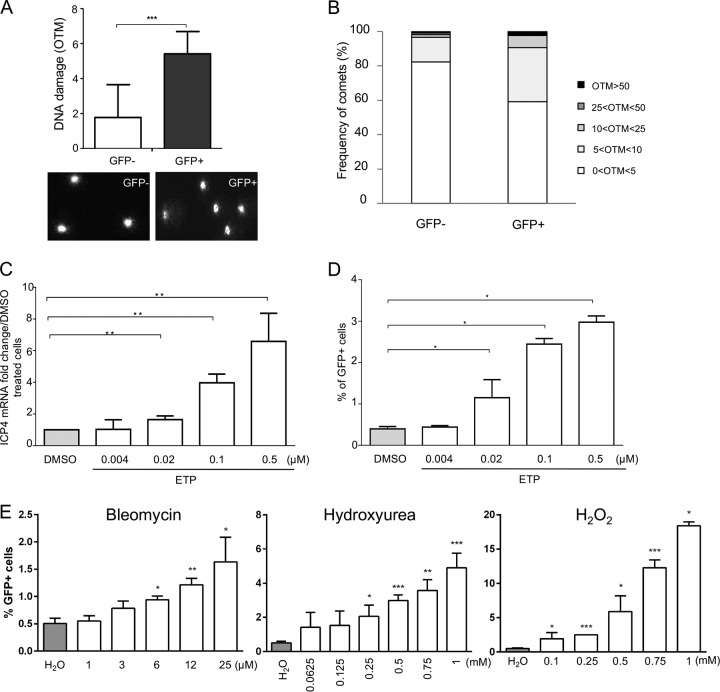
FIG 6.
DNA damage during MDV reactivation. 3867K cells undergoing MDV lytic replication were sorted by cytometry on the basis of the expression of the UL47 gene tagged with EGFP. (A) DNA damage analysis in lytically infected (GFP-positive) and latently infected (GFP-negative) cells. The alkaline comet assay was performed on EGFP-positive and -negative sorted cells. Results are presented as the mean OTM ± SD (***, P < 0.001) (top), and representative comet images are shown (bottom). (B) Frequency distribution of the comets with respect to their OTM values. (C to E) Effect of DNA-damaging pharmacological agents on MDV reactivation. 3867K cells were treated with etoposide (ETP), bleomycin, hydroxyurea (HU), or H2O2 at the indicated concentrations for 48 h. DMSO and H2O were added to the culture media as negative controls. (C) MDV replication was evaluated by quantifying the expression of mRNA for the immediate early gene ICP4 by qRT-PCR. The level of ICP4 expression was normalized to the level of expression of GAPDH, and results are presented as means ± SDs. **, P < 0.005. (D and E) Number of 3867K cells in which MDV was reactivated. The percentage of viable GFP-positive cells (expressing the EGFP-tagged UL47 protein) was determined by cytometry 48 h posttreatment. Viable cells were labeled using the viability dye eFluor 780. Means ± SDs are represented as bars. *, P < 0.05. Results are representative of those from 3 independent experiments realized in triplicate.