Figure 2.
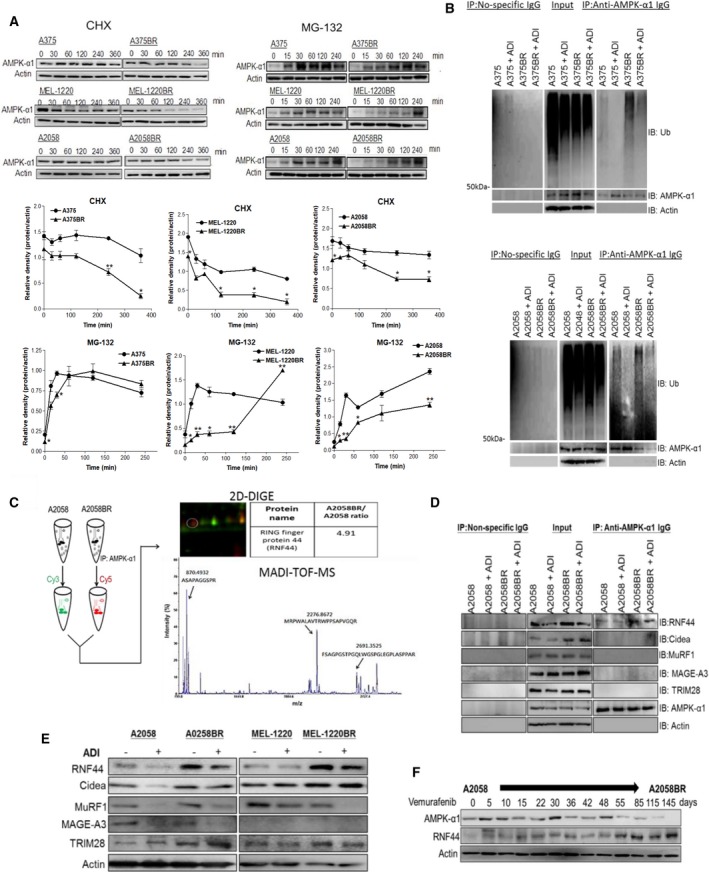
The E3 ligase RNF44 is implicated in UPS of AMPK‐α1 degradation in BR cells. (A) Parental cell and BR cells were incubated with MG‐132 (10 μm) and CHX (80 μg·mL−1), respectively. Cell lysates were collected at different time intervals, and subsequently, AMPK‐α1 was assayed by immunoblotting. The levels of AMPK‐α1 were quantitated by ImageJ and presented as curves. (B) Parental and BR cells were incubated with or without ADI‐PEG20 in the presence of MG‐132 (10 μm) for 4 h. Ubiquitin (Ub) and AMPK‐α1 were separately detected by immunoblotting following immunoprecipitation of AMPK‐α1. (C) The precipitated proteins from A2058 cells and A2058BR cells were, respectively, labeled with Cy3 and Cy5 and then were subjected to 2D gel. Thereafter, the Cy5‐positive spot was identified as RNF44 (Q7L0R7) by MALDI‐TOF MS based on UniProtKB/Swiss‐Prot database. (D) The levels of different E3 ligases (RNF44, Cidea, MAGE‐A3, and MuRF1) in precipitated proteins (D) or total cell lysates (E) were detected by immunoblotting. (F) A2058 cells were constantly treated with vemurafenib (5 μm), and its cell lysates were collected at different time points. The levels of AMPK‐α1, RNF44, or actin were detected by immunoblotting.
