Figure 1.
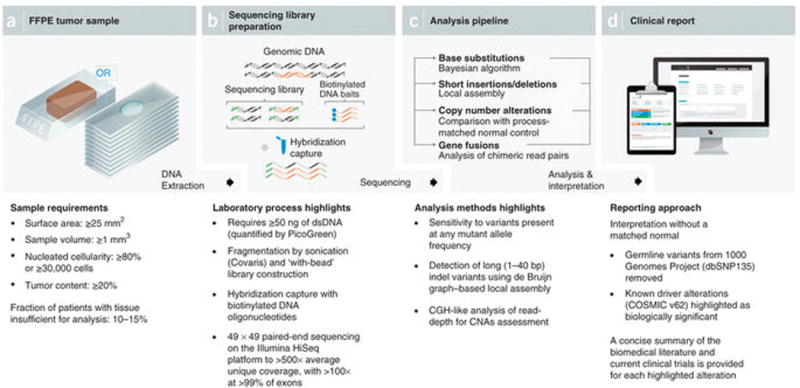
NGS-based cancer genomic profiling test workflow. (a) DNA is extracted from routine FFPE biopsy or surgical specimens. (b) 50–200 ng of DNA undergoes whole-genome shotgun library construction and hybridization-based capture of 4,557 exons of 287 cancer-related genes and 47 introns of 19 genes frequently rearranged in solid tumors. Hybrid-capture libraries are sequenced to high depth using the Illumina HiSeq2000 platform. (c) Sequence data are processed using a customized analysis pipeline designed to accurately detect multiple classes of genomic alterations: base substitutions, short insertions/deletions, copy-number alterations and selected gene fusions. (d) Detected mutations are annotated according to clinical significance and reported.
