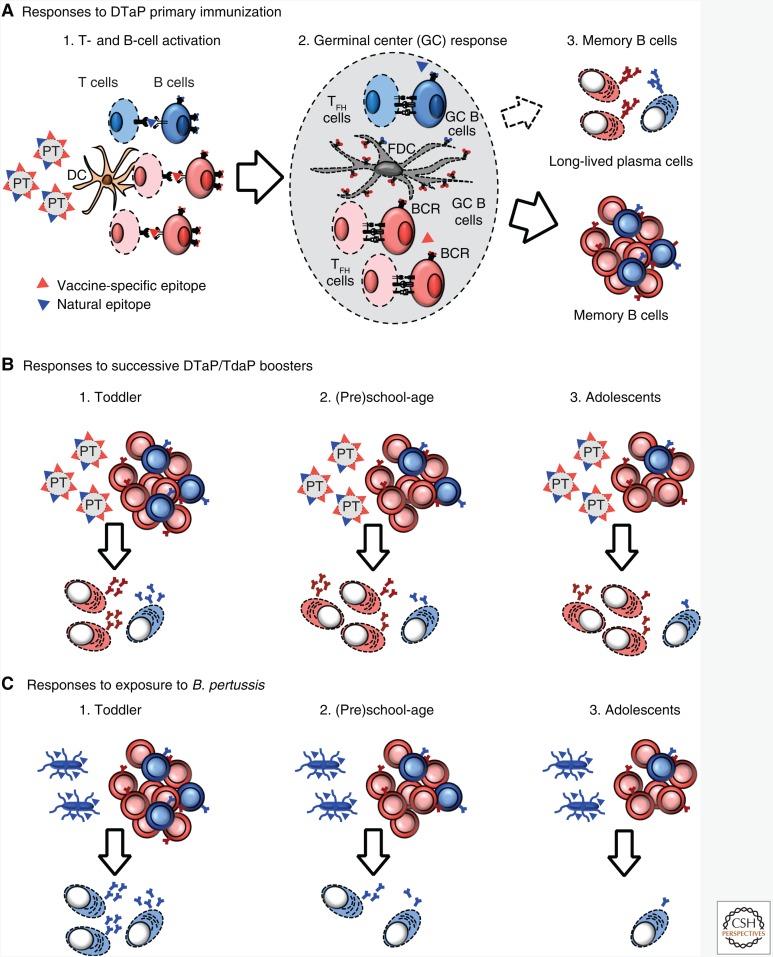
Figure 1.
Pertussis toxin B-cell responses to primary and booster acellular pertussis (aP) immunizations or following exposition to Bordetella pertussis. Immune response to priming with aP (A) leads to formation of anti-pertussis toxin (PT) memory B cells. These are directed either against the epitopes unique to denatured PT (red) or of wild-type PT (blue). Upon boosting (B), the proportion of anti-PT memory B cells specific to wild-type PT declines proportionally to the increasing number of doses (and thus age). Consequently, fewer and fewer wild-type PT-specific B cells are available for reactivation at time of exposure to B. pertussis (C).