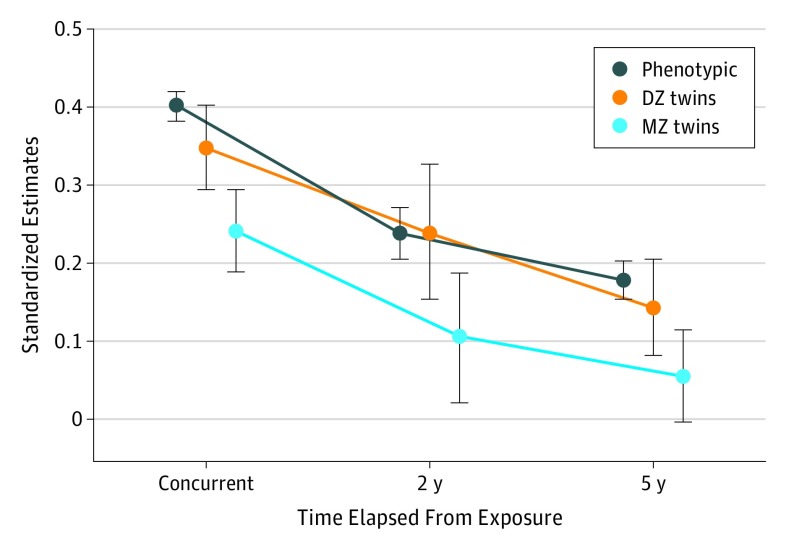
Figure. Longitudinal Contribution of Exposure to Bullying in Childhood to Child-Rated Total Mental Health Difficulties.
The decrease in size from phenotypic estimates to the most stringent monozygotic (MZ) estimates (eg, 3 concurrent estimates) and the decrease of estimates as time from the exposure increases are displayed. Childhood exposure to bullying and mental health outcomes were assessed at the following ages: 11 years (concurrent), 14 and 16 years (2 years), and 11 and 16 years (5 years). The whiskers above and below each estimate indicate the 95% CI. DZ indicates dizygotic.